If you’ve ever worked with APIs, you’ve likely encountered REST and GraphQL. But what exactly are they? And more importantly, when should you choose one over the other? Whether you’re building a simple app or a complex system, deciding between these two can be tricky. Let’s break it down in an easy-to-understand way, as if we’re chatting over coffee.
What Are REST and GraphQL?
First, let’s define these two technologies.
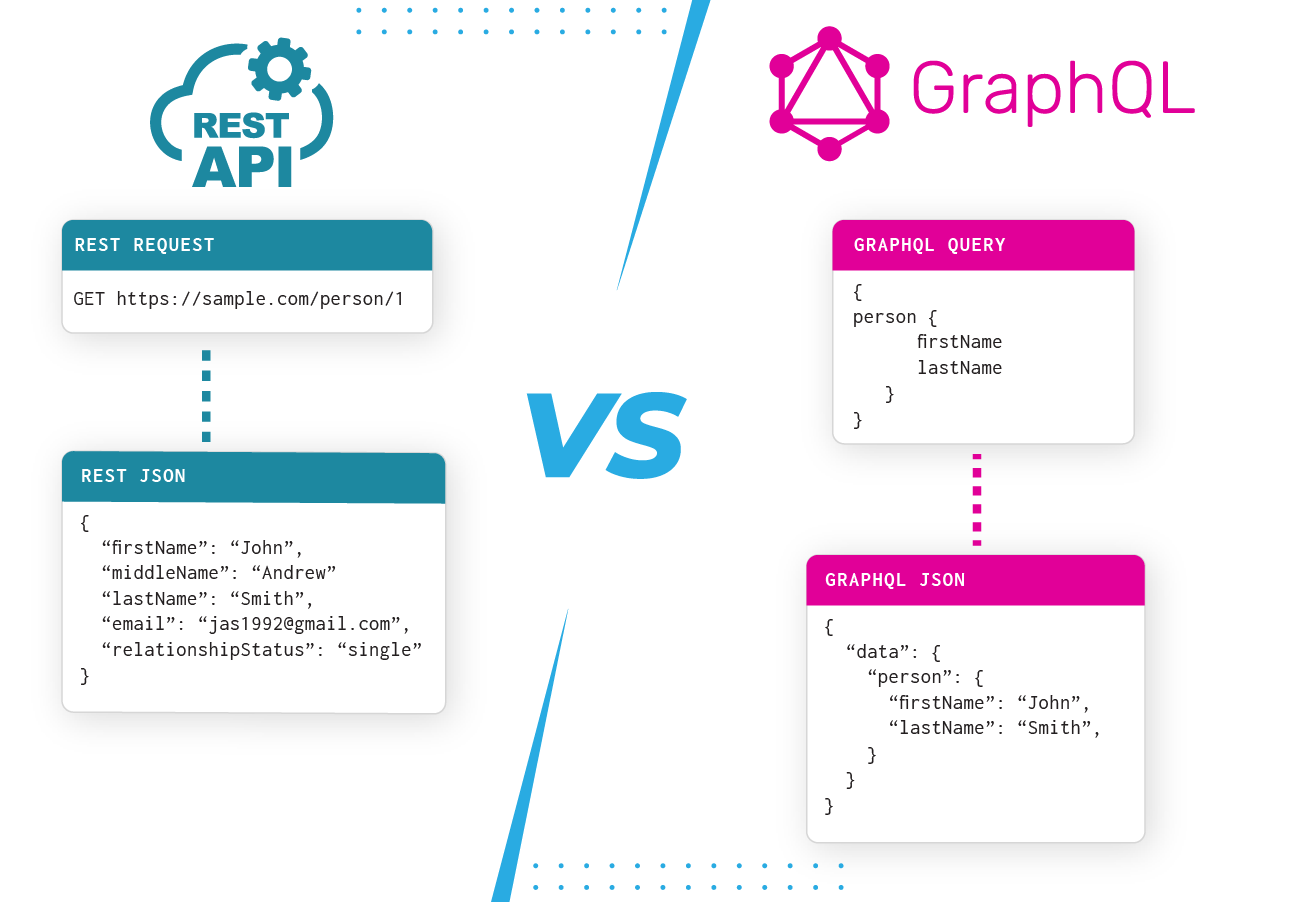
REST stands for Representational State Transfer. It’s an architectural style introduced in the early 2000s that guides how clients (like mobile apps or browsers) interact with servers using URLs and standard HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. REST APIs usually expose multiple endpoints, each corresponding to a resource like /users or /posts.
GraphQL was created by Facebook in 2012 and made public in 2015. It is a query language and runtime for APIs that allows clients to specify exactly what data they need. Instead of multiple endpoints, GraphQL typically uses a single endpoint where clients send queries that describe the shape and amount of data required.
Source: GraphQL Official Documentation
Fundamental Differences Between REST and GraphQL
The main difference lies in how the two approaches handle data delivery.
| Aspect | REST | GraphQL |
|---|---|---|
| API Endpoint | Multiple endpoints based on resources | Single endpoint for all queries |
| Data Fetching | Fixed structure; may lead to over- or under-fetching | Flexible queries; fetch exactly what’s needed |
| Data Structure | Defined by the server | Defined by the client’s query |
| HTTP Methods | Uses GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc. | Typically uses POST for queries and mutations |
| Versioning | Versions like v1, v2 common | No explicit versioning; queries evolve over time |
| Error Handling | Uses HTTP status codes | Returns errors within the response body |
REST: Multiple Endpoints with Fixed Responses
In REST, each resource has its own URL. For example, a GET request to /users returns a list of users in a fixed format determined by the server. The server controls what data is included.
One common drawback is over-fetching — clients often receive more information than they need. For instance, your app might only need a user’s name and ID but gets the full user profile including address and phone number. This extra data can slow down your application and increase bandwidth usage.
On the other hand, under-fetching can happen when the server’s response doesn’t include all the data the client requires, forcing multiple requests.
Source: Fielding Dissertation on REST
GraphQL: Single Endpoint with Precise Queries
GraphQL lets clients specify exactly what data they want by sending a query that mirrors the desired data structure. For example, a query can request just the name and ID of users, and the server will return only that information.
This approach eliminates the issues of over- and under-fetching common in REST APIs. It also reduces the number of requests needed, since clients can request related data in a single query.
Source: GraphQL Official Documentation
When to Use REST vs. GraphQL
Choosing between REST and GraphQL depends on your project’s requirements and constraints.
Use REST If…
- Your API is straightforward or CRUD-focused. REST’s structure aligns well with simple applications where each resource maps neatly to an endpoint.
- You want built-in support for HTTP caching. REST APIs benefit from existing HTTP caching mechanisms, which can improve performance without extra work.
- You need clear, standardized API behavior. REST’s reliance on HTTP methods and status codes provides predictable patterns widely understood across teams.
- You’re working with existing RESTful services. Many external APIs and tools are REST-based, making integration easier if you stick to REST.
Use GraphQL If…
- Your frontend needs more control over data. GraphQL allows clients to tailor responses precisely to UI needs, avoiding unnecessary data transfer.
- You want to reduce multiple API calls. GraphQL queries can fetch related data in one request, simplifying client logic.
- Your data requirements are complex or evolve frequently. GraphQL’s flexible schema lets you adapt queries without changing API versions.
- You prefer a strongly typed schema. GraphQL schemas define types explicitly, helping catch errors early and improving tooling support.
Summary
REST and GraphQL both have their strengths and ideal use cases. REST’s simplicity and widespread adoption make it a solid choice for many applications, especially those with straightforward resource models. GraphQL offers greater flexibility and efficiency for complex or rapidly evolving APIs where clients need precise control over data.