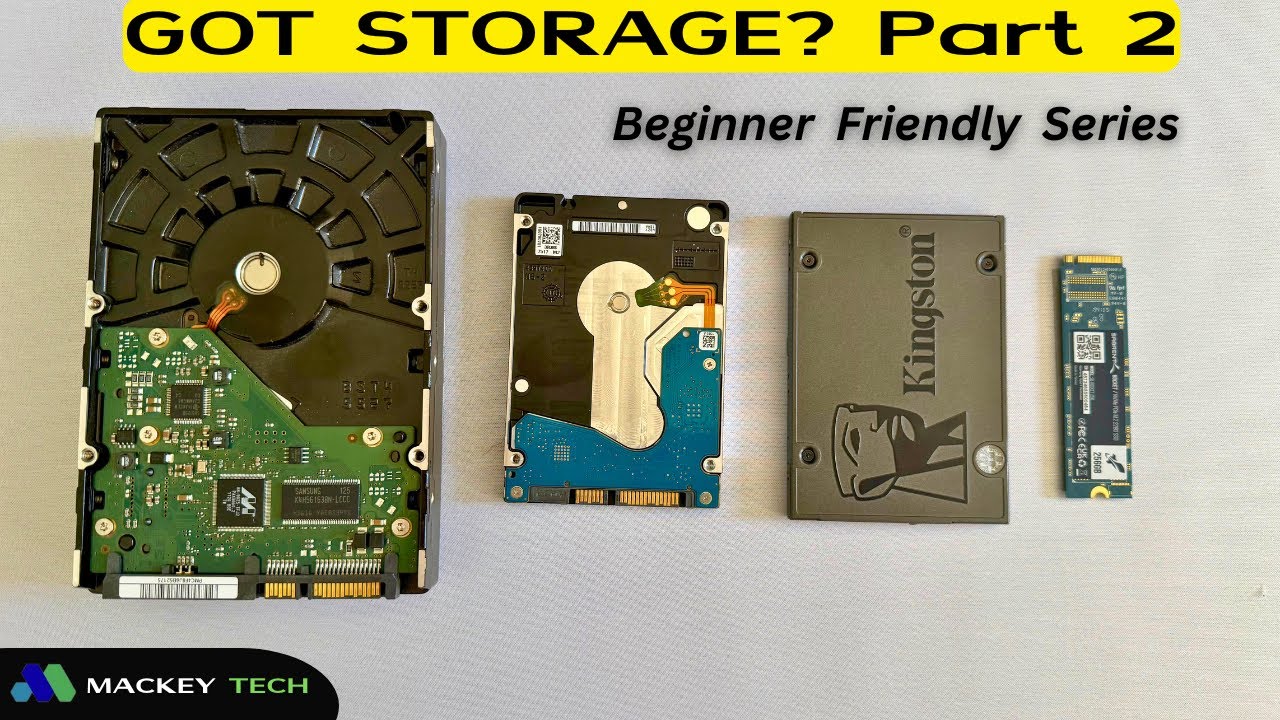
If you’re diving into the world of computer storage, you’ve probably bumped into two terms that sound similar but aren’t the same thing: SSD and NVMe. It’s easy to get confused, especially since they often come up when people talk about making their computers faster. So, what’s the real difference between SSD and NVMe? How does one improve the other? And do you even need to worry about them both?
Let’s break it down, step by step.
What is SSD? What is NVMe? Clearing Up the Confusion
What Exactly Is an SSD?
SSD stands for Solid State Drive. Simply put, it’s a type of storage device that holds your data—like your photos, games, and operating system—without any moving parts. Unlike the older mechanical hard drives (HDDs) that have spinning disks, SSDs use flash memory chips to store data, which makes them faster, quieter, and more durable.
If you’ve ever upgraded your laptop or desktop from an HDD to an SSD, you know the difference immediately: your computer feels snappier, programs load faster, and everything just runs smoother. SSDs fundamentally changed how we experience computers.
What About NVMe?
NVMe, which stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express, isn’t a type of drive itself. It’s actually a protocol—a set of rules that your computer uses to communicate with a storage device.
Think of it like this: If your SSD is a car, NVMe is the highway that lets it zoom. NVMe is designed specifically for SSDs to talk faster and more efficiently to your computer through the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) bus, which is a high-speed interface inside your machine.
So, NVMe is a communication standard used by some SSDs to improve how quickly data can be sent back and forth.
The Core Difference: SSD vs NVMe in Simple Terms
| Feature | SSD | NVMe |
|---|---|---|
| What it is | A storage device | A communication protocol/interface |
| Speed | Faster than HDDs, but varies | Much faster than SATA-based SSDs |
| Interface | Commonly SATA or PCIe | Uses PCIe interface only |
| Supported devices | SATA SSDs, NVMe SSDs, etc. | Only certain PCIe SSDs |
| Compatibility | Works with most computers | Requires motherboard support |
| Example | Samsung 860 EVO (SATA SSD) | Samsung 970 EVO Plus (NVMe SSD) |
In other words: All NVMe drives are SSDs, but not all SSDs use NVMe. Think of NVMe as a faster lane on the PCIe highway, while many SSDs still use the slower SATA road.
How Does NVMe Improve SSD Performance?
If you’ve ever wondered why NVMe SSDs are so hyped, here’s the scoop.
SATA vs PCIe: The Hardware Highway Difference
Most traditional SSDs use the SATA interface, which was originally created for slower mechanical drives. SATA tops out at around 600 megabytes per second (MB/s)—which sounds fast, but remember, SSDs are capable of much more.
On the other hand, NVMe SSDs connect directly to the PCIe lanes on your motherboard, which can offer multiple gigabytes per second (GB/s) of bandwidth. For example, PCIe 3.0 x4 NVMe drives can hit speeds around 3,500 MB/s, and PCIe 4.0 drives can double that!
From Queues to Commands: Why NVMe is Faster
The magic of NVMe also lies in how it handles data requests. SATA was designed to handle 1 command queue with 32 commands. NVMe, however, supports 64,000 command queues with 64,000 commands each. This means NVMe can handle way more data simultaneously, making it a champion for multitasking and heavy workloads.
Imagine you’re a busy chef (the CPU) placing orders for ingredients (data). SATA can only process a few at a time, while NVMe is like having dozens of assistants taking many orders at once—your kitchen runs much smoother.
Real-World Speed Difference
In everyday use, NVMe SSDs dramatically reduce boot times and speed up file transfers and program launches. For gamers, this translates to faster load times and smoother gameplay, especially when dealing with huge game files like those in Cyberpunk 2077 or Call of Duty.
According to Tom’s Hardware, NVMe drives can be 3 to 5 times faster than SATA SSDs depending on the task [1].
Are All NVMe Drives SSDs? Understanding the Overlap
The short answer: Yes, all NVMe drives are SSDs.
Here’s why.
NVMe is a protocol designed specifically for solid-state storage. You won’t find an NVMe-based hard disk drive because mechanical drives just can’t use that high-speed interface.
But not every SSD uses NVMe. Many SSDs use the SATA protocol instead simply because they’re designed to be compatible with older hardware or to keep costs down.
So, if someone says “NVMe drive,” you can safely assume they mean an SSD that uses the NVMe protocol over PCIe.
Are NVMe Drives Compatible With Your Computer?
One of the biggest headaches when upgrading or buying an SSD can be hardware compatibility. You might wonder, “Will this NVMe drive even work in my laptop or PC?”
What to Check Before Buying
- Motherboard Support: Ensure your motherboard supports M.2 PCIe NVMe drives. Many newer models do, but some older ones only support SATA M.2 SSDs or none at all.
- Form Factor: NVMe drives typically come in M.2 form factor, which looks like a small stick about the size of your thumb. Some motherboards require an adapter card for PCIe NVMe SSDs if they don’t have an M.2 slot.
- BIOS/UEFI: Your system firmware (BIOS or UEFI) needs to support NVMe booting if you want to use the NVMe drive as your main boot device.
If your laptop or desktop doesn’t support NVMe, you’re not out of luck—you can still use a SATA SSD, which will definitely beat a mechanical disk.
Benefits of Using NVMe Over Traditional SSDs
Why bother with NVMe at all? Here are the perks:
- Speed: NVMe drives offer significantly faster read/write speeds, loading programs, games, and files much quicker.
- Lower Latency: They respond faster to data requests, which improves overall system responsiveness.
- Better Multitasking: The higher command queue depth in NVMe means better performance when juggling multiple applications.
- Energy Efficiency: Newer NVMe SSDs are often more power-efficient, which can help laptops get better battery life despite their speed.
- Future-Proofing: NVMe technology is becoming the industry standard, so investing in NVMe now means your system will stay relevant longer.
SSD vs NVMe: Which One Should You Choose?
If you’re upgrading your laptop or building a PC, how do you pick between SATA SSD and NVMe?
When to Choose SATA SSD:
- You have an older computer without NVMe or PCIe M.2 support.
- You’re on a tight budget—SATA SSDs are generally cheaper.
- You want a simple drop-in replacement for a hard drive.
When to Choose NVMe SSD:
- Your system supports NVMe and PCIe M.2.
- You want significantly faster speeds for gaming, video editing, or heavy multitasking.
- You want to future-proof your system.
FAQ: Clearing Up Common Questions
Q1: Can I use an NVMe SSD like a regular SSD?
Yes, but only if your computer supports NVMe. Otherwise, it won’t recognize the drive.
Q2: Is NVMe only for desktops?
Nope! Many modern laptops support NVMe SSDs, especially gaming and ultrabooks.
Q3: Will NVMe SSDs make my computer twice as fast?
Not exactly. You’ll see massive improvements in storage tasks, but general speed also depends on other parts like CPU and RAM.
Q4: Are NVMe drives more expensive?
Usually, yes, but prices have been dropping steadily.
Wrapping Up: Understanding Your Storage
So, next time you see “SSD” and “NVMe,” remember: SSD is the type of storage device, and NVMe is a way that some SSDs communicate with your computer to get blazing fast speeds.
If you’re upgrading, check your system’s compatibility first. And if you want the fastest storage possible, an NVMe SSD is the way to go.
Got an older machine? Don’t worry—SATA SSDs are still a huge step up from hard drives. But if your motherboard supports it, NVMe will let your computer feel way snappier.
References
[1] According to Tom’s Hardware (https://www.tomshardware.com/reviews/nvme-ssd-performance) NVMe drives can be several times faster than SATA SSDs, allowing for much quicker data transfer and multitasking.