When you’re diving into networking, the moment you hear “TCP” and “UDP,” it can sound like alphabet soup. So, what are these protocols anyway? And why does it matter which one you use? Let’s break it down in a way that’s easy to digest, whether you’re setting up a chat app, streaming videos, or just curious about how the internet actually works.
What Are TCP and UDP Protocols?
Imagine you want to send a letter. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are like different mail services you can choose for your letter delivery.
- TCP is the reliable, “registered mail” option. It checks to make sure your letter arrives safely—and even if a page goes missing, it’ll resend it. Your message gets delivered in the right order, no surprises there.
- UDP is more like dropping postcards in the mailbox. There’s no guarantee they’ll reach the destination, or arrive in order. But it’s quick, with less overhead.
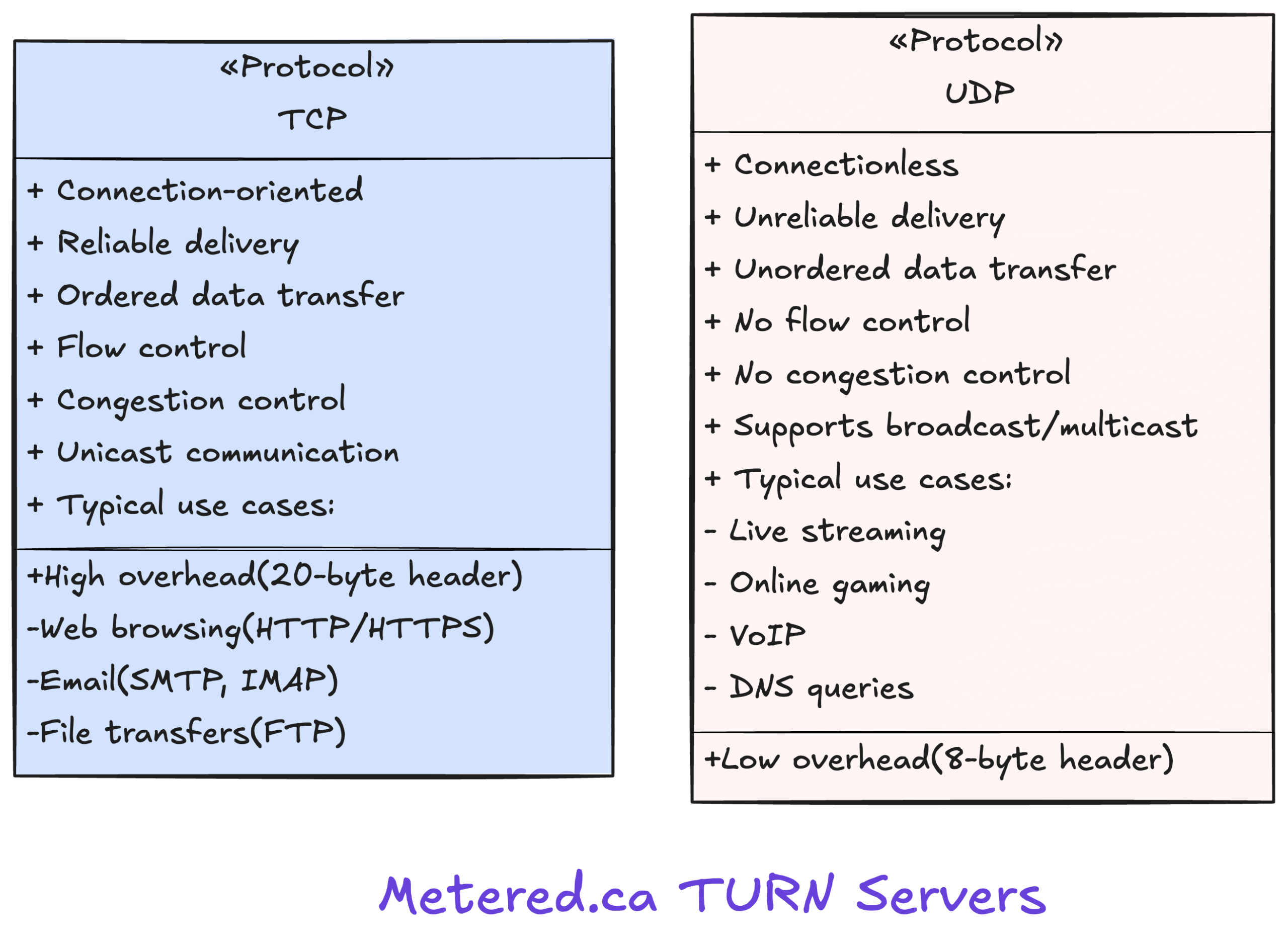
In technical terms, both TCP and UDP are transport layer protocols used in the Internet Protocol Suite. They help send data between computers over networks, but they do so differently. TCP is connection-oriented, meaning it establishes a connection before sending data and keeps track of everything. UDP is connectionless—it just sends packets without checking if they’re received or in proper order.
Think of TCP like a phone call—you dial, get connected, talk, and hang up. UDP is more like shouting across a room—you send the message but don’t know if anyone heard it.
How Do TCP and UDP Differ in Terms of Reliability?
This is where things get interesting. Reliability is often the biggest factor when choosing between TCP and UDP.
TCP and Its Reliability
TCP is designed to be reliable. It uses several methods to make sure your data arrives intact:
- Acknowledgments: After the receiver gets data, it sends back an acknowledgment.
- Retransmission: If the sender doesn’t get an acknowledgment, it resends the data.
- Ordering: TCP numbers the packets, so they’re reassembled in the right order.
- Flow Control: It prevents the sender from overwhelming the receiver.
Because of these features, TCP is great for applications where missing or out-of-order data is unacceptable. Say you’re sending an email or loading a website—imagine if chunks of the page were missing or scrambled.
UDP and Its Unreliability
UDP skips these reliability steps. It sends packets (called datagrams) without checking if they arrive or if they arrive in order.
Why would anyone use that? Because speed matters in some cases. UDP has less overhead, which means it’s faster and more efficient, especially on networks where packet loss is minimal.
Think about live streaming or online gaming. Getting the latest data fast is more important than missing a few packets. If a second of video lags, you want the next one right away, not to wait for the missing pieces.
When Should I Use TCP vs UDP?
Figuring out which to use can feel confusing—especially when you’re building a project and want it to run smoothly.
Use TCP When…
- You need guaranteed delivery. Applications like web browsing, emails, and file transfers need every byte to arrive.
- Order matters. TCP ensures data is reassembled as it was sent.
- You want error checking built-in. TCP handles retransmissions and flow control.
Example: When you download a file, TCP ensures no bits are missing or scrambled.
Use UDP When…
- Speed is king. Real-time applications like video calls, online games, and streaming prioritize low latency.
- Tolerate some data loss. Missing a few packets won’t ruin the experience (like a skipped frame in video).
- You can handle reliability yourself or don’t need it. Some applications have their own error correction on top of UDP.
Example: In multiplayer games, if a player’s position update is lost, the next update will likely fix it. Waiting for a missing packet would just cause lag.
Quick Table: TCP vs UDP Use Cases
| Application Type | TCP (Reliable) | UDP (Fast) |
|---|---|---|
| Web browsing | ✔️ | |
| ✔️ | ||
| File transfer | ✔️ | |
| Live video streaming | ✔️ | |
| VoIP calls (Skype, Zoom) | ✔️ | |
| Online gaming | ✔️ | |
| DNS Queries | ✔️ (usually) |
Notice: While DNS primarily uses UDP for speed, it can fall back to TCP if the response is too big—another example of using the right tool for the job.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of TCP and UDP?
Alright, let’s get into the pros and cons. This will help clear up which protocol fits your needs better.
TCP Advantages
- Reliable delivery: No data gets lost or arrives out of order.
- Error correction and flow control: Manages network congestion and ensures smooth communication.
- Widely supported: Almost all networks and devices support TCP.
TCP Disadvantages
- Slower performance: The extra checks and acknowledgments add delay.
- More overhead: TCP headers are larger, so it uses more bandwidth.
- Connection setup: Establishing a connection before data transfer takes time (the “three-way handshake”).
UDP Advantages
- Speed: It’s faster since there’s minimal error checking.
- Less overhead: Smaller headers mean less bandwidth usage.
- Simple: No connection setup — just send and forget.
UDP Disadvantages
- No reliability: Data can get lost or arrive out of order.
- No built-in error correction: The application has to handle errors.
- Not ideal for critical data: You can’t trust UDP for important files or messages.
Addressing Common Pain Points
When Should I Pick TCP or UDP?
Think about your application’s priorities. If you’re building a chat app where every message counts, go TCP. If it’s a live streaming app, UDP might be your best bet.
Understanding Technical Jargon
Don’t let terms like “connection-oriented” or “packet loss” scare you. “Connection-oriented” just means TCP sets up a virtual handshake before chatting. “Packet loss” is when some data gets dropped on the way, like a lost postcard.
How Does Protocol Choice Affect Performance?
Choosing TCP makes sure nothing breaks but adds delay. UDP speeds up transmission but may lose bits. It’s a trade-off: do you want reliability or speed? Sometimes, you want a bit of both.
FAQs About TCP and UDP
Q: Can UDP be reliable?
A: UDP itself isn’t reliable, but applications can add their own checks on top of UDP to improve reliability if needed.
Q: Why do games prefer UDP?
A: Because fast updates are more important than perfect data. Lag is worse than missing a small update.
Q: Can TCP be used for video streaming?
A: Yes, but buffering and latency might increase since TCP waits for missing data.
Q: How do I decide which one to use in my project?
A: List your needs: Is data accuracy critical? Use TCP. Is speed and low latency essential? Use UDP.
Wrapping Up
Choosing between TCP and UDP isn’t about right or wrong—it’s about matching your project’s needs. TCP’s got your back when you need reliability and order. UDP takes the lead when speed and efficiency matter.
Next time you build something that uses the network, ask yourself: What’s more important here—making sure every single packet arrives, or just getting the data there fast? That simple question will guide you to the right protocol.
Remember, no protocol is perfect, but knowing these differences helps you make smarter choices—and that’s what good networking’s all about.
References
[1] According to Cisco, TCP ensures reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of data between applications running on hosts communicating via an IP network. Source: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/about/press/internet-protocol-journal/blogs/201404.html
[2] According to Cloudflare, UDP is a simpler, faster, but connectionless protocol that doesn’t guarantee message delivery or ordering. Source: https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ddos/glossary/user-datagram-protocol-udp/
[3] According to GeeksforGeeks, TCP is preferred for applications where reliable communication with error recovery is required, whereas UDP is used in applications like video streaming where speed is more crucial than reliability. Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-tcp-and-udp/