If you’ve ever poked around inside your computer or smartphone’s settings, you might have come across the terms RAM and ROM. They sound similar and both are types of memory, but they serve very different purposes. Understanding the difference between RAM and ROM can feel confusing at first—especially when tech jargon starts flying around like it’s a foreign language. Don’t worry, we’ll break it all down in a super simple, conversational way. By the time you finish reading, you’ll know exactly why your device needs both, how they work differently, and what that means for your everyday use.
What Is RAM and What Is ROM?
Let’s start with the basics:
- RAM stands for Random Access Memory.
- ROM stands for Read-Only Memory.
Sounds simple, right? But what does that actually mean?
What Is RAM?
Think of RAM as your computer’s short-term memory. It’s where your device stores the stuff it’s actively working on right now. When you open an app, load a file, or browse the internet, your computer loads that information into RAM so it can access it quickly.
The key thing with RAM is that it’s volatile. This is tech-speak for: as soon as you turn off your device or it loses power, everything stored in RAM disappears. So, RAM doesn’t hold onto information permanently—it’s a temporary workspace.
What Is ROM?
ROM, on the other hand, is like the long-term memory inside your device. It stores essential instructions that your device needs to start up and function. Unlike RAM, ROM is non-volatile, meaning it doesn’t lose its data when the power goes off.
For example, the firmware that tells your computer how to boot up or the basic instructions on your smartphone’s motherboard are stored in ROM. You can’t just “overwrite” ROM easily because it’s meant to be permanent or at least semi-permanent.
So, in a nutshell:
- RAM = temporary, fast workspace.
- ROM = permanent, essential instructions.
How Do RAM and ROM Differ in Function?
Alright, now that we know what they are, what do they actually do differently?
RAM: The Active Workspace
Imagine you’re cooking a recipe. RAM is like your kitchen counter where you keep all your ingredients and tools you’re currently using. It needs to be big and clear enough so you can move fast and not slow down your cooking.
When you run a program, your device copies the data into RAM. This way, the processor can grab information at lightning speed without having to dig through slower storage like your hard drive or SSD. The more RAM you have, the more tasks and apps your device can handle at once without getting bogged down.
ROM: The Instruction Manual
ROM is like the recipe book you keep on the shelf. It’s not something you change frequently, but without it, you wouldn’t even know how to start cooking. The computer’s BIOS or firmware is stored in ROM—it tells your device how to boot up and prepare everything so you can get to the fun stuff (like using apps).
Once your device is up and running, ROM takes a backseat. It’s just quietly sitting there, ready to help if needed, but it’s not involved in your daily computing tasks.
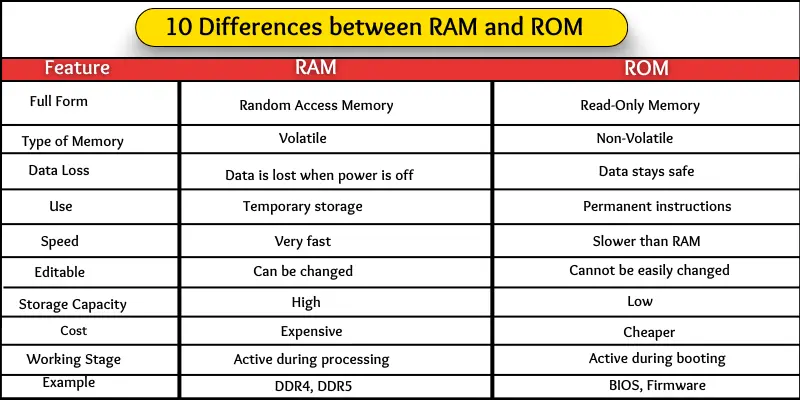
| Aspect | RAM (Random Access Memory) | ROM (Read-Only Memory) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Temporary workspace for running programs | Permanent storage of essential instructions |
| Volatility | Volatile (loses data when off) | Non-volatile (retains data without power) |
| Function | Stores data currently in use | Stores firmware and boot processes |
| Speed | Fast access for quick operations | Slower than RAM but sufficient for startup |
| Capacity | Typically larger (4GB to 64GB+) | Usually small (a few MBs to GB) |
| User Modification | Can be changed by running apps | Usually not changed by users |
What Are the Typical Uses of RAM Versus ROM?
You might ask: if they’re so different, what exactly do we use each for? Let’s get practical.
Common Uses of RAM
- Running applications: When you open a web browser or video game, data gets loaded into RAM for quick access.
- Multitasking: More RAM lets you switch between apps smoothly.
- Temporary storage: Helps with buffering videos or loading large files quickly.
- Gaming and graphics: RAM is crucial because games need to access tons of data fast.
For example, if you’re editing photos in Photoshop, the program loads your image into RAM so you can make changes without waiting forever. Without enough RAM, your computer might freeze or slow down, leaving you frustrated.
Common Uses of ROM
- Booting your device: ROM stores the firmware that tells your device how to start.
- Embedded systems: Devices like microwaves, calculators, and even your car use ROM to store the software they need without user modification.
- Device firmware updates: ROM can sometimes be updated (with care), but this isn’t a daily thing.
Think about your smartphone. When you turn it on, the ROM kicks in to start the operating system. Without ROM, your phone wouldn’t know how to power up or load the OS.
How Do RAM and ROM Affect Computer Performance?
You’ve probably heard people say, “You need more RAM to speed up your computer.” But what role does ROM play in all this?
RAM’s Impact on Performance
RAM is your device’s multitasking hero. When you have more RAM:
- You can run more apps at the same time.
- Switching between programs feels smoother.
- Complex tasks like video editing or gaming become less laggy.
If your RAM fills up, your computer has to swap data to slower storage (called “paging” or “using virtual memory”), which can seriously drag performance down.
For example, if you try running a heavy video editing program on a laptop with only 4GB of RAM, you’ll notice lag. Adding more RAM means the device can hold more data in the quick workspace, making everything snappier.
ROM’s Impact on Performance
ROM doesn’t affect daily performance the way RAM does since it mainly holds startup instructions. However, if your firmware (stored in ROM) is outdated or buggy, it can cause system crashes or failure to boot.
Also, certain devices have a type of ROM called Flash memory which acts as permanent storage for your operating system and apps. While it’s technically non-volatile storage, it’s more related to storage devices like SSDs rather than classic ROM chips.
Clearing Up Common Confusions About RAM and ROM
Volatile vs Non-Volatile Memory—What Does That Mean?
This term trips up a lot of beginners. In simple words:
- Volatile memory loses everything when power goes off (RAM).
- Non-volatile memory keeps data even without power (ROM).
Why does this matter? Because RAM’s volatility is what lets it be so fast—it doesn’t waste time saving data permanently, so it focuses on speed.
Why Do Devices Need Both?
You might wonder, “Why can’t everything just be stored in one type of memory? Why the hassle?”
The answer: speed and function. RAM is super-fast but temporary. ROM is slower but permanent.
If your device only had ROM, it would be like trying to cook a meal using only a recipe book—good luck chopping veggies without a counter! And if it only had RAM, it wouldn’t remember the recipe when you started.
So, your device uses ROM for the essential startup and basic instructions, and RAM to keep things moving fast while you work.
Quick FAQ About RAM and ROM
Q1: Can I upgrade my RAM and ROM?
A: You can usually upgrade RAM on many computers to improve performance. ROM, especially firmware, is rarely upgraded manually and usually done via software updates.
Q2: Does more ROM mean better performance?
A: Not really. ROM size isn’t related to performance like RAM is. It just needs to hold the necessary firmware.
Q3: Is the storage on my phone’s internal memory ROM?
A: The internal storage is a type of non-volatile memory (flash storage), but technically, ROM refers to read-only firmware storage. So, it’s related but not exactly the same.
Q4: What happens if RAM is full?
A: Your device starts using slower hard drive space as temporary RAM, which slows everything down.
Wrapping It Up: Why Both RAM and ROM Matter
Think of your device as a busy office:
- RAM is the desk where all the current work happens—papers, files, your coffee mug. You need a big desk to work efficiently.
- ROM is the filing cabinet with the important instruction manuals that you don’t change but always need access to.
Without RAM, your device would crawl like a snail, struggling to keep up with tasks. Without ROM, your device wouldn’t even know how to start in the first place.
So next time you see “RAM” and “ROM,” you’ll know they’re both essential but play totally different roles. Knowing this helps you understand why upgrading RAM can make your computer faster, but ROM stays quiet in the background, making sure your device boots and runs smoothly.
References
[1] According to TechTerms, RAM is volatile memory used for temporary storage while ROM is non-volatile and stores permanent data. (https://techterms.com/definition/ram)
[2] Computer Hope explains RAM’s role in running programs and ROM’s function in booting devices. (https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/r/ram.htm)
[3] HowStuffWorks breaks down the difference between volatile and non-volatile memory types. (https://computer.howstuffworks.com/ram.htm)
[4] Lifewire discusses how RAM size impacts multitasking and device speed. (https://www.lifewire.com/what-is-ram-5182904)