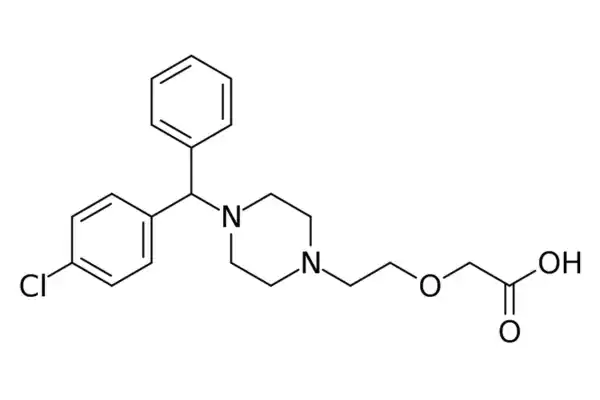
Brief overview of Cetirizine
Cetirizine, a second-generation antihistamine, is used for the relief of allergy symptoms. In many countries, it is available as both a prescription drug and an over-the-counter (OTC).
Cetirizine is briefly described below:
- Mechanism: Cetirizine blocks the action of histamine. Histamine is a substance that the body produces in response to allergies. Cetirizine works by blocking histamine. Histamine is a natural substance produced by the body in response to allergies.
- Indications: Cetirizine can be used to treat a variety of allergic conditions including:
-
- Hay fever (seasonal allergic rhinitis)
- Perennial allergic rhino rhinitis
- Allergic conjunctivitis is an eye allergy
- Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (chronic Hives)
- Dosage: The recommended dose of Cetirizine varies depending on the age and condition being treated. It is usually taken once daily, either in liquid or tablet form.
- Duration: Cetirizine starts to work within 20-60 minutes of ingestion, and offers relief for 24 hours.
- Common Side Effects: include drowsiness, dry mouth, headaches, and stomach upset. Cetirizine is generally well tolerated and considered safe.
- Warning: Cetirizine can make some people drowsy, especially when they need to be alert. For example, if you are driving or operating heavy equipment.
- Drug interactions: While Cetirizine is unlikely to interact with other medications, you should consult your healthcare provider if you are taking any other medication or have medical conditions.
- Special populations: It’s generally safe to use during pregnancy or breastfeeding. However, it is recommended that you consult your healthcare provider prior to use. Individuals with kidney disease may need to adjust their dosage.
- Availability: Cetirizine can be purchased as both a prescription drug and an OTC product under various brand names or generics, making it available to a broad range of consumers.
This is only a general overview. Specific instructions and suggestions should be obtained from your healthcare provider or product labeling.
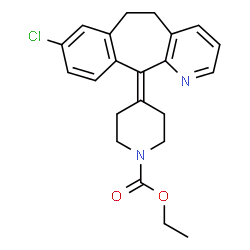
A brief overview of Loratadine
Loratadine, a second-generation antihistamine widely used for treating allergy symptoms, is known to be effective. Here is a quick overview of Loratadine.
- Mechanism: Loratadine is an antihistamine that works by blocking histamine. Histamine is a substance produced by the body when it has an allergic reaction. Loratadine works by blocking histamine. It relieves symptoms such as sneezing and itchy, watery, or runny noses, as well as throat and nasal itching.
- Indications: Loratadine treats a variety of allergic conditions including:
-
- Hay fever (seasonal allergic rhinitis)
- Perennial allergic rhino rhinitis
- Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (chronic Hives)
- Dosage: The recommended Loratadine dosage is usually determined by age and condition. It is typically taken once daily in liquid or tablet form.
- Duration: Loratadine provides relief for allergy symptoms about 24 hours after it is taken. Loratadine is known for its nondrowsy formula, which means that it is less likely to cause drowsiness than some older antihistamines.
- Common Side Effects: Loratadine’s side effects are mild, but may include headaches, dry mouth, and stomach discomfort. Loratadine is a less sedative antihistamine than older antihistamines. This makes it the preferred choice of people who must remain alert.
- Precautions: Loratadine generally is well tolerated but should be used with caution by individuals who must remain alert when operating heavy machinery or driving.
- Drug interactions: While Loratadine is unlikely to interact with other medications, you should consult your healthcare provider if you are taking any other medication or have medical conditions.
- For special populations: Loratadine can be used safely during pregnancy or breastfeeding. However, it is best to consult with a doctor before taking it. Individuals with kidney disease may need to adjust their dosage.
- Availability: Loratadine can be purchased as a prescription drug and also in a variety of generic and brand-name forms.
Loratadine, a long-lasting allergy medication, is popular due to its effectiveness and low likelihood of causing sleepiness. However, as with all products, you should always consult your healthcare provider for specific instructions.
Cetirizine and Loratadine table of comparison
Here’s a table comparing Cetirizine and Loratadine:
| Aspect | Cetirizine | Loratadine |
| Mechanism of Action | Blocks histamine receptors, reducing allergy symptoms | Blocks histamine receptors, reducing allergy symptoms |
| Indications | Seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, chronic idiopathic urticaria | Seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, chronic idiopathic urticaria |
| Dosage | Typically once daily | Typically once daily |
| Onset of Action | 20-60 minutes | 1-3 hours |
| Duration of Action | Approximately 24 hours | Approximately 24 hours |
| Drowsiness | May cause drowsiness in some individuals, although less likely than older antihistamines | Generally considered non-drowsy, but minimal drowsiness can occur |
| Common Side Effects | Dry mouth, headache, stomach upset | Headache, dry mouth, gastrointestinal discomfort |
| Precautions | Caution when operating heavy machinery; more likely to cause drowsiness in some individuals | Caution when operating heavy machinery; generally less likely to cause drowsiness |
| Drug Interactions | Low potential for interactions, but consult a healthcare provider if taking other medications | Low potential for interactions, but consult a healthcare provider if taking other medications |
| Special Populations | Pregnancy and breastfeeding-safe uses; dose adjustments may be necessary in individuals with kidney conditions. | Generally safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding; dosage adjustments may be necessary for individuals with kidney problems |
| Availability | Available as prescription and OTC; various brand names and generic forms | Available as prescription and OTC; various brand names and generic forms |
Please be aware that each person’s response to medication can differ. It is important to follow any specific instructions given by your healthcare provider, or those on the packaging. It’s also a good idea to speak with a doctor before taking any new medication, or if there are specific concerns about your health.
Importance of understanding the differences between the two
There are several reasons why it is important to understand the difference between Loratadine and Cetirizine:
- Personalized treatment: Because people respond to medication differently, healthcare providers can tailor treatments to meet individual needs. Understanding which medication is best for a patient’s allergy symptoms can be improved by knowing the drug that works best.
- Minimizing side effects: By understanding the differences between the two medications, patients and healthcare professionals can choose the drug that is least likely to cause certain side effects such as drowsiness. This can improve patient safety and comfort.
- Optimizing Effectiveness: For some individuals, one medication may be more effective than another for specific allergy symptoms. Patients can select the medication that offers them the most relief by understanding these differences.
- Preventing Drug Interactions: Knowing about potential drug interactions between Loratadine and Cetirizine can help prevent dangerous interactions with other medications that a patient may be taking.
- Cost considerations: In some cases cost can be an important factor when choosing between medications. Knowing the differences in price between Cetirizine and Loratadine can help patients and healthcare professionals make more cost-effective decisions.
- Accessibility: Based on your region and health care system, you may find that one of these drugs is more easily available or covered under insurance. Understanding the availability of medications can affect your choice.
- Special Populations: Certain groups such as children and elderly people, pregnant women or nursing mothers, and certain other groups may require special considerations in the use of medication. It is important to know which medications are safer or better suited for these groups.
- Adherence: Patients will adhere better to their treatment plans if they know the differences between drugs and why one particular medication was selected for them. Better adherence results in better symptom control.
- Treatment options: Patients may have tried a medication and had limited success, or experienced unwanted side effects. Understanding the differences between Cetirizine and Loratadine can provide alternative treatment options to those who need them.
- Making Informed Decisions: At the end of the day, making informed decisions is crucial in healthcare. Patients who are aware of their treatment options and the differences in medications can make more informed decisions about their healthcare. They will also be able to work better with their doctors.
Understanding the differences between Cetirizine (Loratadine) and Cetirizine is crucial for tailoring allergy treatments, optimizing efficacy, minimizing side effects, and ensuring cost-effective and safe care. This information empowers both patients and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding allergy symptom management.
Mechanism of Action
Both Loratadine and Cetirizine are second-generation antihistamines that relieve allergy symptoms.
Here is an explanation of the mechanism of action of these devices:
Mechanisms of action for Cetirizine and loratadine:
- Histamine Antagonist: Both Cetirizine, and Loratadine are antihistamines. Histamine is produced naturally by the body when it experiences an allergic reaction. Histamine is responsible for symptoms such as sneezing and runny or watery noses, as well as itchy or watery eyelids, or itching in the nose or throat.
- Blocking histamine receptors: When an allergen triggers a reaction, histamine releases and binds with specific receptors, known as H1-receptors, on cells of various tissues, such as those in the skin and respiratory system. This binding results in the typical allergy symptoms.
- Inhibition Histamine Effects: Cetirizine and loratadine block (antagonistic) these H1 receptors. They prevent histamine binding to the receptors and thus the histamine effects on target tissues.
- Reduction of Allergy symptoms: This receptor blockade relieves the symptoms that are caused by histamine such as sneezing and itching. It also reduces runny nasal passages and watery eyelids. This relieves common allergic reactions such as allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, and urticaria.
- Receptors with Limited Effects: Second-generation antihistamines such as Cetirizine or Loratadine have been designed to reduce the impact of other receptors. This is especially true for those located in the central nervous system. This design minimizes the sedative (drowsiness-inducing) effects commonly associated with older antihistamines.
Cetirizine, Loratadine, and other antihistamine medications work by blocking histamine. Histamine is the main mediator of allergic reactions. They do this by antagonistic H1 receptors in target cells. These medications are effective for treating allergies because they reduce allergy symptoms by blocking histamine.
Indications and Approved Uses
Both Loratadine and Cetirizine are antihistamines that have been approved for:
- Seasonal Allergy Rhinitis: Relief from symptoms such as sneezing and runny eyes caused by seasonal allergies (e.g. pollen).
- Perennial Allergy Rhinitis: Treatment for year-round allergic rhino rhinitis due to indoor allergens.
- Allergic conjunctivitis: Treatment of eye allergy symptoms such as itching or redness.
- Chronic Urticaria Idiopathic: Alleviation of chronic hives with their associated itching.
These medications can be used to treat a variety of allergic conditions and provide relief from the symptoms.
Onset and Duration of Action
Cetirizine (and Loratadine) have the following onset and duration:
Cetirizine:
- Onset of Action: Cetirizine usually starts acting within 20-60 minutes of ingestion.
- Duration: Cetirizine’s effects last approximately 24 hours and provide relief for allergy symptoms throughout the day.
Loratadine:
- Start of Action: Loratadine typically starts working between 1-3 hours following ingestion. However, it can take longer than Cetirizine.
- Duration: Loratadine’s effects last approximately 24 hours.
Cetirizine is known to have a long-lasting effect, which makes it a convenient option for a once-daily dose of Loratadine.
Safety and Side Effects
Cetirizine:
- Safety: Cetirizine, when taken in the recommended doses, is considered safe by most people.
- Side Effects Common: Side effects common may include headache, nausea, and fatigue.
- Drowsiness: Although Cetirizine may cause less drowsiness compared to older antihistamines it is still possible for some people to become drowsy. It is recommended that you exercise caution when driving heavy machinery or operating any other equipment until your individual response has been determined.
- Serious but Rare Side Effects: Even though rare, some people may experience serious side effects, such as allergic reactions or liver issues. If you experience any unusual or serious symptoms, seek medical attention.
Loratadine:
- Safety: Loratadine, when taken as prescribed, is well tolerated and generally considered safe by most people.
- Side Effects Common: Side effects are common and include dry mouth, headaches, and stomach discomfort.
- Sleepiness: Loratadine does not cause drowsiness in most people. It is less likely than older antihistamines to cause drowsiness.
- Rare But Serious Side Effects: Although rare, serious side reactions such as severe skin reactions or allergic reactions can occur. Seek medical attention if unusual or severe symptoms develop.
Follow the dosing recommendations and contact your healthcare provider if any side effects are concerning. Inform your healthcare provider about any medical conditions you have or medications that you take to ensure the safety of the medication.
Drug Interactions
Drug Interactions :
Cetirizine, as well as Loratadine, are considered to be low-risk medications for interaction with other drugs. To ensure your safety and avoid any potential drug interactions, you should consult with a pharmacist or healthcare provider, particularly if you take other medications.
Here are a few key points about drug interactions:
- Central Nervous System Decay: Cetirizine or Loratadine may enhance the effects of central nervous system depressants such as alcohol, medications that cause sleepiness, and other drugs. Combining these substances can lead to an increase in sedation and impaired coordination. When using these substances together, you should exercise caution.
- CYP450 enzyme inhibitors: The liver is the primary organ responsible for metabolizing both drugs. Although they are less likely than older antihistamines to interact with drugs inhibiting cytochrome P450, interactions still occur. When using drugs that affect liver enzymes, it’s best to consult your healthcare provider.
- Other Allergic Medications: Combining Cetirizine and Loratadine, whether prescribed or over-the-counter, can increase the risk of adverse effects, without adding any additional benefit. Multiple antihistamines should not be taken at the same time.
- Specific Medicines: Certain specific medications such as ketoconazole, an antifungal, and erythromycin, an antibiotic, may inhibit the metabolism of Cetirizine or Loratadine. This could lead to higher levels of the drugs in the blood. If necessary, healthcare providers can adjust dosages.
- Health Conditions: People with specific medical conditions and allergies should tell their doctors about their medical history including their current medications to ensure that they are safe when using Loratadine or Cetirizine.
- Over-the-counter products: Use caution when taking multiple over-the-counter medications. They may contain ingredients that interact with Cetirizine and Loratadine. If you are unsure, always read the label and ask a pharmacist for advice.
While Cetirizine or Loratadine generally have low interaction potential, individual reactions can vary. Consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist before using Cetirizine and Loratadine with other medications or supplements.
Conclusion
Cetirizine and Loratadine are effective antihistamines for managing allergy symptoms. While they share similar mechanisms of action and indications, they may differ in terms of onset, duration, and potential side effects.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best option based on individual needs and medical history to ensure safe and effective allergy relief.