Scholarships and Grants: Scholarships and grants are different, even though they both provide money for tuition and other expenses. Let’s first define these two words. Students receive money as scholarships to help them pay for their education. Grants can also be money given for different purposes. The two are similar because they both provide money to students that don’t need to be paid back, unlike student loans. Experts say that students should exhaust all free funding sources before applying for a loan. The main difference between a grant and a scholarship is that grants are awarded to institutions, while most scholarships go to individuals. Let’s examine the other differences between these two words through this article.
What Are Grants?

Grants are free financial assistance provided by federal or state governments for students based on need. Students must show proof of limited income to receive these funds, with grants specifically given to low-income students to cover college costs.
Each academic year, the federal government allocates a specific sum to be distributed as grants. Funds will be dispersed on a first-come, first-served basis until funds have been exhausted; applying early gives you a higher chance of getting your desired grant amount. Two tools used by the government for dispersal include Federal Supplemental Educational Opportunity Grant (FSEG) and Pell Grants – two programs used to award eligible students with financial assistance from grants.
To qualify for federal financial aid, you must complete the FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid). This form includes student loans, grants, work-study opportunities, and institutional aid.
Sources of grants?
Grant funding comes from various sources such as government agencies, private foundations, research institutes, and non-profit organizations.
Here are a few common grant sources:
- Government Agencies: Federal, state, and local government entities often offer grants to support initiatives, research projects, and community development efforts. Some examples of such grant programs are those provided by the National Institutes of Health, National Science Foundation, United States Department of Education, and Environmental Protection Agency.
- Private Foundations: Private foundations are philanthropic organizations that support many different causes and projects. These foundations may be created by individuals, families, or corporations and some notable examples include Bill and Melinda Gates Foundations, Ford Foundations, Rockefeller Foundations, and Open Society Foundations.
- Corporate Grants: Many businesses and corporations provide grants to support the various corporate social initiatives of their business or corporation, such as education, health care, environmental conservation efforts, the arts & culture as well as any other activities aligning with company values.
- Research Institutions: Universities and colleges as well as research institutions offer grants to fund academic research, scientific studies, and other forms of research activities. These grants may be used for expenses associated with equipment purchase, data collection, or personnel costs associated with this research activity.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Organisations specializing in specific causes or fields frequently award grants to individuals, groups of community members or organizations in their focus area – often to support healthcare, social services or education initiatives.
- Art and Cultural Organizations: Arts councils and cultural foundations offer grants to performers, artists, and arts organizations. These grants may be used for exhibitions, performances or residencies as well as arts education programs or residencies.
- Philanthropic Programmes: Individuals or families can organize philanthropic initiatives and programs that offer grants to organizations or individuals pursuing specific goals, or making positive contributions to society. Such grants could focus on education, poverty reduction, human rights protection, or community development efforts.
- International Organizations: International organizations, including the UN, World Bank, and regional development banks often grant money for initiatives and projects which promote sustainability, poverty reduction, healthcare provision, education, and humanitarian efforts.
Individuals and organizations seeking grants should conduct extensive research in order to locate funding sources that match up with their program or project goals. Keep in mind that each grant source has its own eligibility criteria, guidelines, and application processes that should be carefully observed when seeking grants.
Types of grants?
Individuals, organizations, and research institutions alike can all apply for various grants.
Here are a few commonly-available grants:
- Federal Grants: Federal government agencies offer grants that support various initiatives including scientific research and education, healthcare development, social service provisioning, environmental conservation efforts, and community building. Grant programs may include those offered by the National Institutes of Health Grants, National Science Foundation Grants, or Department of Education grants.
- State Grants: State governments provide grants to support projects and programs within their jurisdiction, with grants typically providing funding for education, health care, economic development, arts & culture, or environmental conservation activities. Programs tailored specifically to local priorities & needs.
- Institutional Grants: Colleges and universities may award institutional grants to support academic programs, research projects, faculty development initiatives, scholarships for students, and infrastructure improvements. These grants may only be made available internally at an institution or externally to other individuals or organizations.
- Research Grants: These grants are specifically tailored to assist specific scientific or academic projects, typically sponsored by research-oriented organizations, private foundations, or government agencies. With these grants in hand, researchers are able to conduct studies, collect data for analysis purposes, and ultimately make significant advancements within their respective fields.
- Program-Specific Grants Program: specific grants provide funding for specific sectors or areas, such as education, healthcare, arts & culture, environmental conservation, social services & community development. Nonprofits, government agencies & private foundations that specialize in this area typically offer these grants.
- Nonprofit Grants: Foundations and charities offer grants to programs and projects which meet their missions or focus areas, whether that be non-profit organizations, groups in the community, or even individuals working towards goals that align with those of the grantor organization. These grants may be given out directly or through intermediary organizations like foundations.
- Project Grants: Project grants provide support for specific projects within research, education, community development, and other fields. The grants cover costs related to implementation such as equipment, materials, and personnel costs.
- Community Grants: Community grants are intended to fund projects that will directly benefit a particular community or region, such as healthcare access, economic growth, infrastructure improvements, or social services in an area. They can be used in support of areas like healthcare access, economic expansion or infrastructure improvement within an individual location.
Be mindful that eligibility and grant availability will depend on both purpose and source. Each grant program may have specific guidelines and an application process; before making your decision on any one grant application it’s wise to carefully research and examine all details involved.
What is the application process for grants?
Grant application processes vary based on both the grantee and grant program.
Below are a few steps you can take when applying for grants:
- Discover Grants: Start by researching grants that fit with the objectives and goals of your organization or personal life. Check government agencies, foundations, research institutes, nonprofits, or other grant sources; use online databases or resources offered by grant-giving organizations; find suitable grant opportunities using directories of grants available online – then get to work!
- Examine Grant Guidelines: Carefully review each grant you’re interested in for eligibility criteria and requirements, including project focus areas and geographic restrictions as well as deadlines.
- Preparing a Grant Proposal, Most grants require applicants to submit a grant proposal, which should typically include these elements:
- Executive Summary: Give an executive overview of your project, organization, or business that emphasizes its significance, purpose, and expected results.
- Project Description: Present an organized description of your project that details its goals, objectives, activities, and methods in an easy-to-read format. Provide a timeline and indicate how it meets grant goals as well as any requirements specified in the guidelines.
- Budget: To create an accurate project budget and allocate grant funds appropriately. Include matching funds or in-kind donations requested as well as any matching grants requested and any matching donations in-kind contributions that might exist.
- Plan of Evaluation: Create an evaluation plan outlining how you’ll measure and assess the success of your project, including indicators, data-collection methods, and tools that will be utilized when assessing the results of this endeavor.
- Organismal Information: Outline information about your organization including its history, mission, past achievements, and capacity to complete projects. Attach any supporting documents like financial statements or annual reports as appropriate.
- Gather Required Documents, Grant applications often require additional documents in addition to their grant application form, such as:
- Documents related to your organization: These may include legal documents, tax exemption certificates (if applicable), and board member and organizational policy details.
- Financial documents: Include financial statements, budgets, and other records as proof of the transparency and stability of your organization’s finances.
- Request letters of support: Ask partners, collaborators, and community stakeholders to vouch for your project’s significance and feasibility by signing letters of support on its behalf.
- Follow-Up: After submitting a grant application, it’s wise to confirm with the grant provider that they received it. Some programs require extra steps such as site visits, interviews or clarification requests so be prepared with any additional information requested and fulfill any other requirements necessary.
Guidelines and instructions for grant recipients should be thoroughly read and followed, with each grant program having its own criteria and requirements. When creating your grant proposal, ensure it explains your project’s importance, feasibility, and potential impact in an engaging and accessible way.
What benefits of grants?
Individuals, communities, and organizations all can take advantage of grants for various reasons. Grants offer numerous advantages.
Grants provide financial assistance for research, projects, programs, or operational costs of individuals or organizations – including salaries, equipment costs, materials costs, training costs infrastructure costs as well as any other necessary expenses – to allow them to pursue their goals while making positive contributions in their communities. Grants relieve individuals and organizations of financial burden while helping them meet their goals and make lasting contributions that contribute positively to society.
Grants provide evidence of viability and significance to projects while attesting the organization that awarded it as a supporter and endorser, further increasing credibility and reputation. Grant funding may also enhance how others perceive an individual or an organization’s work, creating more support from partnerships or potential collaboration opportunities.
Grants provide additional resources and capacity that would not otherwise be available, giving individuals and organizations additional capacity and resources that allow them to improve their capabilities, purchase necessary equipment, hire new staff members, conduct research, or create innovative programs more quickly and more efficiently than before. Grants help individuals and organizations achieve their goals faster and more efficiently.
Grant-funded projects typically involve collaborations and partnerships between organizations and experts, often through grant-funded initiatives. Networking through these grant-funded initiatives can result in invaluable connections, knowledge-sharing, and future collaboration opportunities that strengthen an individual or organizational network and open up new possibilities.
Research and Innovation, Grants play an essential role in supporting innovation and research. They support scientific studies, academic advances, and creative endeavors by researchers, scientists, innovators, and others who wish to explore new ideas or solve pressing issues using grants as funding sources.
Social Impact and Community Development, Grants that go to community-focused organizations or projects can have an immense impact on society. Such grants support initiatives addressing education, healthcare, and social services; environmental conservation; arts & culture development, and economic growth – among other matters. Individuals and groups benefiting from grants can meet critical needs more quickly while making positive changes within their communities.
Grants are an excellent way to support professional development. Grants may be used to fund training programs or workshops, conferences, or mentoring initiatives; all with the goal of increasing knowledge, skills, and expertise among organizations and individuals for improved performance.
Grants for sustainable projects and initiatives can play an essential role in driving long-term change. Grants provide individuals and organizations with financial assistance for long-term solutions with long-term impacts and benefits, furthering environmental conservation, social empowerment, and economic growth for a more sustainable future.
Grants come with obligations and responsibilities for recipients; grant recipients typically must provide progress reports on how funds were utilized efficiently. Grants of all sorts, both financial and otherwise, can make a dramatic difference in the success of organizations, individuals, and communities alike.
What Are Scholarships?

Scholarships are a form of financial aid that is free, but distinct from grants. They can be funded in many different ways by large corporations, small businesses, and local communities; the vast majority are awarded on merit alone; but others may reward athletic abilities or extracurricular achievements or simply being taller than certain heights.
Some scholarships are awarded based on merit, such as high school grades or athletic ability. Other scholarships require multiple requirements that you meet before being considered, such as being of a certain race/ethnicity/field of study/gPA requirements/completing essays, etc.
Scholarships are highly competitive and hundreds of students may compete for each scholarship; competition for larger ones will only increase as more applicants apply. To win one of these large awards, an impressive academic record with a high GPA and extracurricular activities must also be demonstrated.
Smaller or local scholarships tend to be less competitive, making you more likely to win them. Although winning multiple smaller scholarships won’t provide as much money overall, winning several smaller ones can add up over time.
Sources of scholarships?
Students may apply for scholarships from multiple sources.
Below are several of these scholarship resources:
- Universities and Colleges: To attract and support talented students, many universities and colleges provide scholarships tailored specifically for them. Scholarships may be awarded on the basis of academic performance, talent, or athletic accomplishment, among other criteria.
- Government Agencies: Government agencies on a federal, state, and local level often offer scholarships to students. Scholarships may be awarded based on academic achievement, financial need, or minority status.
- Private Foundations and Organizations: Many private foundations and organizations provide scholarships for students from various fields. This may include corporations, community groups, professional associations, or philanthropic organizations – with some scholarships targeting specific groups such as women, minorities, or those living on low incomes.
- Professional Associations: Many professional organizations offer scholarships for students pursuing degrees within their fields. These awards aim to support and encourage those who share a particular profession or industry with similar passions.
- Cultural and ethnic organizations: These organizations offer scholarships to students from diverse ethnic and cultural backgrounds in order to promote diversity and strengthen education within local communities.
- Community and Nonprofit Organisations: Local community organizations, nonprofits, and charitable groups may offer scholarships for students in their area to achieve specific goals such as community service, leadership development, or service to others.
- Scholarships sponsored by employers: Some companies provide scholarship funding for dependents or children of employees as a way of relieving some financial pressure from families of workers. This may ease the financial strain on these families.
Databases that compile scholarship information from various sources make it possible for students to search for scholarships that match their interests and qualifications. Students should search and explore all available scholarship resources in order to identify those that best meet their goals, qualifications, and interests.
Types of scholarships?
Students may apply for various scholarships available to them. With many types of awards to choose from, students have plenty of chances to find financial assistance for college studies.
- Merit-Based Scholarships: Merit-based scholarships recognize academic achievement such as high grades or test scores in an area such as music or arts, or exceptional talent displayed through music lessons or arts practice. A merit-based scholarship recognizes students who have excelled academically.
- Scholarships based on financial need: Scholarships will be granted based on each student’s financial requirements, providing help for those from low-income families needing financial support for further studies. Financial information like income or assets is typically considered when reviewing applications.
- Athletic Scholarships are granted to student-athletes with exceptional talents and abilities. Colleges and universities may provide these awards, which cover tuition fees as well as living costs.
- Scholarships for Creative Excellence: These awards recognize and support students who excel in artistic disciplines such as performing arts, visual arts, creative writing, or filmmaking. This opportunity helps develop students’ talent while rewarding creativity.
- Minority-specific scholarships: These scholarship programs support students from minority backgrounds such as race, LGBTQ+ status, or disability. Their purpose is to promote diversity and inclusion within education.
- Field-Specific Scholarships: These scholarships are tailored toward students pursuing specific studies, including STEM (Science, Technology, and Engineering), education, business, healthcare, or social sciences. This funding encourages them to pursue careers and financial support in these fields.
- International Scholarships: These scholarships are specifically offered to international students living outside of the country that offers the scholarship, providing financial aid for them to pursue education abroad while encouraging cross-cultural interaction and understanding.
- Scholarships for Community Service: These awards honor students who have demonstrated an exemplary commitment to volunteerism and community service, encouraging them to give back to their local communities through civic engagement initiatives.
Please be aware that these categories are only general in nature; some scholarships will fall into multiple categories. It is crucial that students conduct extensive research on different scholarship opportunities available to them to determine which best matches their goals, interests, and qualifications.
What is the application process for scholarships?
Scholarship programs and organizations with scholarship offerings typically follow different application processes when accepting scholarship applicants.
Here are the steps that you will likely follow when submitting an application:
- Find Scholarships: Begin your scholarship search by identifying scholarships that match your goals, qualifications, and interests. Browse available grants from universities, government agencies, or private foundations; make use of scholarship databases, search engines, or college financial assistance offices; you may even discover unexpected scholarship opportunities!
- Examine Eligibility Criteria: Carefully research each scholarship that interests you to ascertain its eligibility criteria, taking into account factors like academic requirements, your chosen field of study, citizenship status, financial needs or talents, or demographic criteria.
Documents Required, Most scholarship applications require certain documents to be submitted, such as those mentioned here. They could include:
- Personal Statement or Essay: Craft an engaging essay or personal statement that showcases your goals, achievements, and motivations while explaining how this scholarship will assist with reaching these objectives.
- Request letters of recommendation: Teachers, mentors, or employers who know your character and qualifications could write you letters of reference as letters of endorsement.
- Academic records: Include transcripts from your academic record, including grades in high school or college as well as any standardized test scores (SAT/ACT) or other relevant achievements.
- Financial Information: If the scholarship is need-based, additional information such as tax returns and proof of income may be requested from you. Include your resume or Curriculum Vitae (CV), detailing information such as your education, extracurriculars, work experience, and awards.
- Be on time: Make sure that you understand all scholarship deadlines, and submit your applications promptly. It is crucial that you manage your time efficiently; late applications won’t be accepted.
- Follow-Up: Once your application has been submitted, follow up with the scholarship program so that you can ensure its receipt. It is advisable to do this so you can confirm receipt.
Application processes are increasingly competitive, making early starts and organization key components to successfully submitting an application. Make sure you stay abreast of scholarship requirements so you can tailor your application specifically toward meeting them.
Benefits of scholarships
Scholarships provide many advantages to students. Scholarships have many advantages for recipients.
- Scholarships Can Provide Financial Assistance Scholarships provide valuable assistance for education expenses such as textbooks, living costs, and tuition fees. Scholarships reduce or even eliminate the need for personal funds or student loans to cover these costs and relieve some of the financial strain of pursuing higher education.
- Scholarships are an honor and sign of distinction, celebrating a student’s talents or achievements and increasing his or her standing with peers, teachers, and potential employers. Scholarships help build their reputation among classmates, instructors, and employers as well.
- Access to Education, Scholarships provide access to higher education that might otherwise be out of reach for some students, enabling them to attend top universities or participate in special programs.
- Scholarships Reduce Student Debt, Scholarships can reduce student debt, unlike loans, scholarships do not require repayment and can help students reduce their reliance on them – ultimately leading to a reduction of debt after graduation.
- Enhancing Networking and Connections, Many scholarship programs provide networking opportunities, mentoring programs, or alumni networks that enable individuals to engage with professionals, peers, mentors, and potential opportunities for mentorship or guidance that could open doors of success and opportunities.
- Scholarships often have conditions attached, such as maintaining an acceptable GPA or engaging in extracurricular activities, that encourage academic excellence as well as personal and leadership development. By fulfilling these expectations and requirements, scholarships provide incentives that encourage academic excellence as well as participation in activities that foster personal growth and leadership potential.
- Confidence and Self-Esteem Increased, Receiving a scholarship recognizes a student’s abilities, potential, and dedication; this boosts self-confidence as it validates all their hard work while instilling feelings of accomplishment and pride in them.
- Scholarships provide an avenue for students to advance their careers by providing internships, research experiences, workshops, or conferences that enrich knowledge, skills, and resumes – making them more appealing to employers or those pursuing further studies.
Scholarships provide more than financial benefits; they also allow students to recognize, grow, and experience unique opportunities.
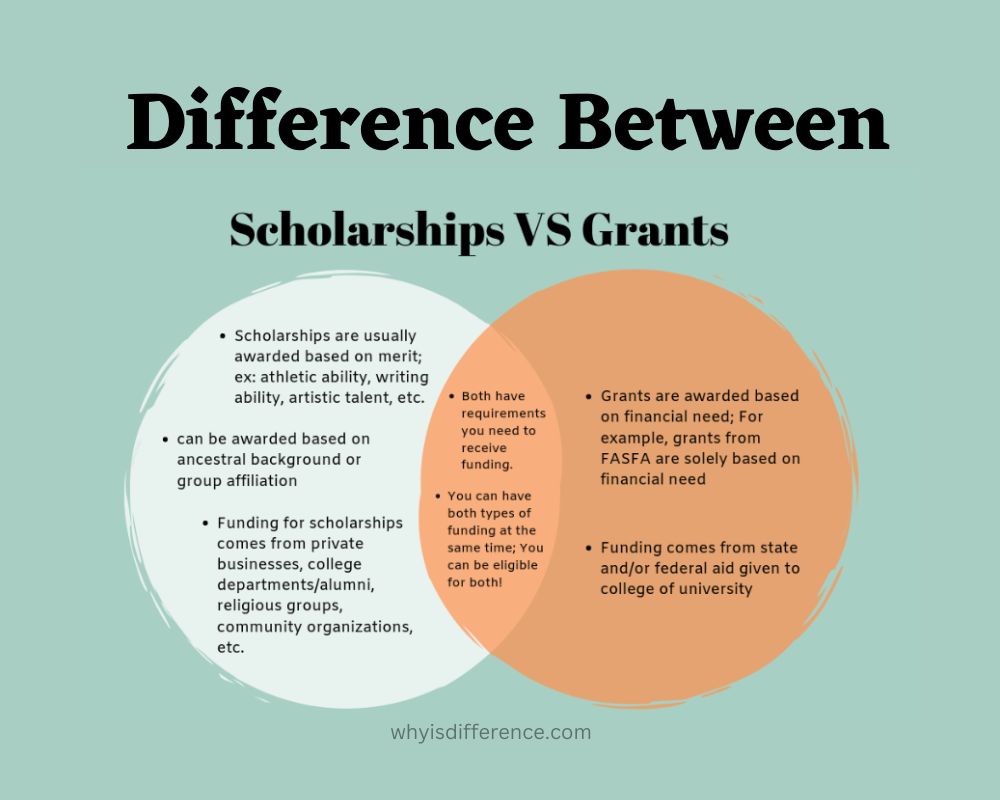
How Scholarships And Grants Are Similar
Both grants and scholarships offer students free money to assist with paying their college tuition costs. One of their most attractive features is that grants and scholarships do not require repayment – no payments, interest rates, or payments are required when receiving grants and scholarships! You keep what is awarded as scholarship money, meaning graduating with less student debt!
Scholarship and grant funds typically only last one academic calendar year, as the majority of awards, do not recur annually; to receive them again each time. Although specific scholarship awards do recur annually; even if awarded one you still must meet its requirements to keep receiving assistance each year.
What is the Difference Between Scholarships and Grants?
You will find that there are numerous differences between scholarships and grants, from eligibility requirements to application processes.
Scholarship Funders Scholarships may be funded by individuals, corporations, small businesses, or non-profit organizations while grants are generally given by state governments.
Criteria for Eligibility
Grants are generally distributed based on financial need. The federal government offers grants for low-income students attending college. To determine eligibility for scholarships and grants, FAFSA forms are used as eligibility indicators.
Eligibility Criteria
Scholarships are given out based on merit. Each funding institution establishes its own criteria for eligibility that can differ from institution to institution. Most often, to become eligible for a scholarship application an applicant must write an essay about an assigned topic.
How Much Financial Aid Are Available for You
The federal government determines your grant entitlement each academic year using data provided from your FAFSA application and personal circumstances. Students who qualify will receive individual grant amounts based on individual needs. Each funding organization will announce a specific award amount. If there are multiple scholarship winners, each of them will receive the same prize amount.
FAFSA Requirements
To become eligible for grants, the FAFSA must be submitted and processed. Your information will then be checked against federal databases to ascertain your eligibility for financial aid of this nature.
How often must I submit the FAFSA for scholarships? That depends on which one it is; while many private scholarships do not require it, you still may want to complete one if applying for merit scholarships at your college or demonstrating need. If an application requires FAFSA certification it must also include this section.
Education Level
Most scholarship organizations only provide scholarships for undergraduate students. Once graduate school is in mind, fellowships become available instead. Grants are available to higher education students at all levels.
Comparison Table Between Scholarships and Grants
| Scholarships | Grants | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial awards are given to students based on merit, need, or other criteria. | Financial awards are provided for specific projects, research, or general funding purposes. |
| Funding sources | Private organizations, foundations, universities, government agencies, etc. | Government agencies, private organizations, foundations, research institutions, etc. |
| Criteria for awarding | Merit, academic achievement, talent, financial need, specific characteristics, etc. | Project proposals, research objectives, innovation, financial need, community development, etc. |
| Types and purposes | Merit-based, need-based, athletic, creative, minority-specific scholarships. | Federal, state, institutional, research, and program-specific grants. |
| Application process | Typically requires an application, essays, recommendation letters, academic records, etc. | The application process may involve project proposals, research plans, budgets, etc. |
| Obligations and requirements | May require maintaining a certain GPA, participating in extracurricular activities, or fulfilling specific criteria. | May have reporting requirements, project deliverables, progress updates, or other specific obligations. |
| Recipients and eligibility | Primarily targeted toward students pursuing education at various levels. | Individuals, organizations, researchers, institutions, non-profit entities, etc. |
| Impact on education | Provides financial assistance, recognition, and access to educational opportunities. | Supports specific projects, research, innovation, and educational initiatives. |
Scholarships Or Grants- Which Is Better?
Both grants and scholarships can be useful, though neither one stands out as superior. Both offer financial aid without charging an upfront cost if they meet certain criteria; you should take full advantage of them both to decrease how much money will be needed to cover education.
College Raptor’s Student Loan Finder helps you discover tailored loan solutions. Compare interest rates and lenders to locate the ideal student loan!
Conclusion
In the end, both grants and scholarships are excellent sources of aid to students seeking higher education. While they often recognize the best qualities and achievements of students while grants focus on the need for financial aid and specifically-focused projects. Both offer invaluable assistance to students, helping them make their academic aspirations more feasible.