North America and South America: When talking about America, one must always ask what exactly separates its two parts. One of the most renowned isthmuses of Panama acts as a divide between Northern and Southern regions, providing shelter to approximately 936 Million people globally. Although initially part of the Southern side, Panama Isthmus now acts as a point of separation.
Definition and Overview of North America
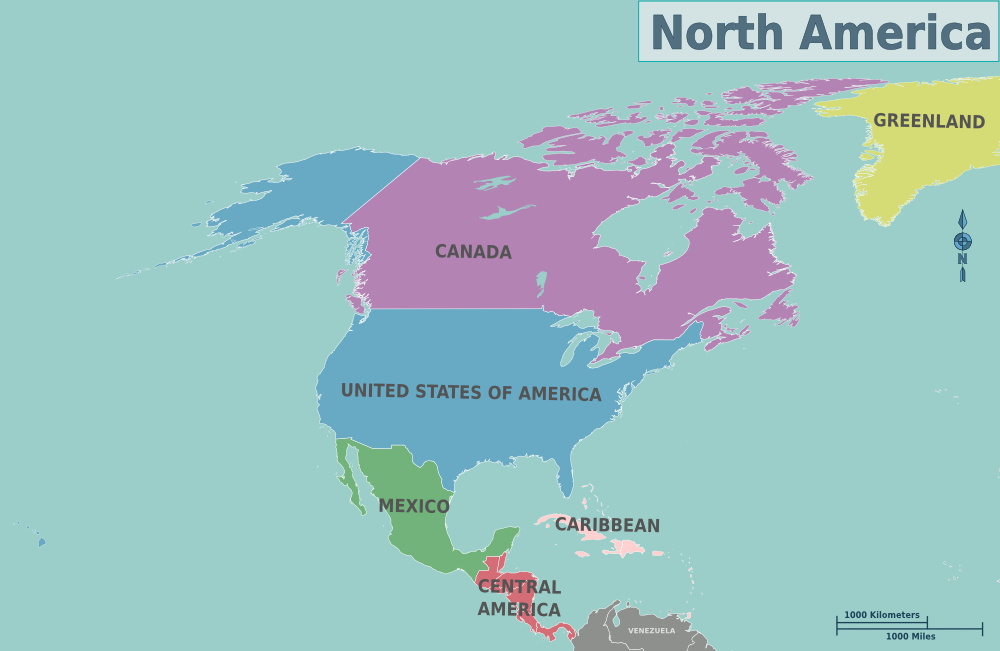
- North America lies predominantly within the western hemisphere of the northern hemisphere and borders both the Arctic Ocean and Atlantic Ocean to its north and east respectively. Covering an estimated surface area of 24.7 million square kilometers, making it the third-largest continent.
- North America comprises several countries, such as the United States (along with Canada and Mexico), Greenland, Denmark, and several Caribbean nations. Mexico and Canada are considered core nations due to their economic and political impact – although Greenland may technically fall outside this definition.
- North America boasts an expansive geography encompassing vast plains, mountain ranges like the Rocky and Appalachian Mountains as well as large bodies of water such as the Great Lakes. North America also features different climate zones ranging from the Arctic climates found in northern Canada to tropical conditions found throughout southern Mexico and the Caribbean regions.
- North America’s history includes advanced civilizations of indigenous people such as Mayas, Aztecs, and Incas who lived here before European colonists arrived. Christopher Columbus arrived in North America near the end of the 15th century followed by British, French, and Spanish colonies settling here shortly thereafter.
- North America’s cultural diversity stems from indigenous traditions as well as waves of immigrants from Europe, Africa, and Asia. English, Spanish, and French are the three primary spoken languages on this continent.
- North America’s economy is diverse and advanced, with strong strengths in technology, finance, manufacturing, and agriculture as well as natural resources. The United States and Canada both rank among the world’s three largest economies; their respective nations also play key roles in regional trade agreements like North American Free Trade Agreement.
- North America is home to democratic nations with diverse political systems. Canada stands out as both a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democratic republic; in comparison, the US is a federalist republic; Mexico features both federalism and presidential in their constitutional republican form.
- North America is home to iconic landmarks like the Statue of Liberty and Niagara Falls. Yellowstone National Park also resides here – making this continent an unparalleled mix of natural wonders, lively cities, and cultural heritage sites as well as recreational opportunities.
- North America as an entire continent boasts diverse landscapes and an enthralling cultural vibrancy and plays an indispensable role in the world economy, politics, and culture.
Definition and Overview of South America
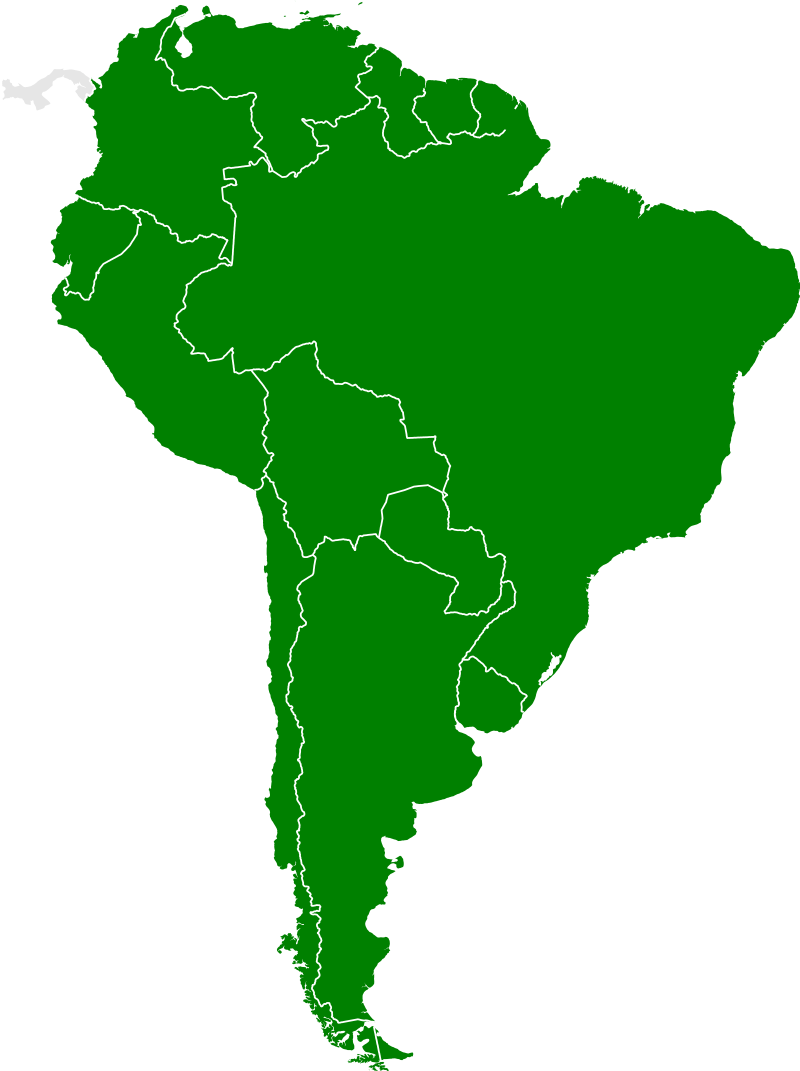
- South America lies predominantly within the western hemisphere in the southern hemisphere and is bordered on either side by either the Caribbean Sea or the Atlantic Ocean, making up approximately 17.8 million square kilometers – ranking it fourth among continents by land area.
- South America consists of 12 nations, such as Brazil and Argentina. Brazil is South America’s most populous nation; Colombia and Argentina follow behind. South America also encompasses other territories like Falkland Island (a British Overseas Territory) and French Guiana, among many others.
- South America is an expansive continent home to an abundance of geographical landmarks, from the Amazon rainforest and Andes mountains to Pantanal wetlands, and the Patagonian Steppe. Additionally, the climate varies dramatically throughout South America from tropical rainforests of the Amazon basin and temperate desert climates of the southern cone.
- South America’s history is defined by ancient civilizations like those found in South America such as Inca, Moche, and Tiwanaku that left behind architectural and cultural legacies that can still be seen today. European colonizers began arriving during the 15th and 16th centuries; predominantly Spanish. Colonization had an immensely negative effect on indigenous populations as colonies were established that exploited natural resources en masse.
- South America is well known for its diverse cultural life. This continent features native traditions, African and Asian influences, European immigrants as well as immigrants from Africa. Spanish, Portuguese, and indigenous languages are among the most widely spoken tongues on South American soil.
- South America’s economy combines agriculture, mining, manufacturing, and services. Brazil leads this region in economic development followed by Argentina and Colombia. South America boasts abundant natural resources including mineral deposits, oil, gas, and fertile agricultural land that have made way for regional economies such as Mercosur (Southern Common Market) and Pacific Alliance to increase trade integration among member countries.
- South America boasts an array of political systems, but democracy remains the predominant form. Brazil and Argentina are federal republics while Chile and Uruguay utilize presidential systems. Venezuela, Ecuador, and Bolivia represent forms of “21st-century socialism”, also known as communism.
- South America is famous for its breathtaking landscapes, such as the Amazon Rainforest, Galapagos Islands, and Iguazu Falls. Additionally, Rio de Janeiro, Buenos Aires, and Machu Picchu offer vibrant city life as well as historical landmarks, outdoor activities, wildlife encounters, and historical experiences that draw people here from across the globe.
- South America, as a continent, boasts outstanding natural beauty, cultural variety, and historical importance. With its diverse geography and deep history spanning millennia – as well as economic potential – South America stands as a crucial component of a global society.
Geographic Location
North America can be found primarily in both the northern and western hemispheres. The continent lies between the Arctic Ocean in the north, the Atlantic Ocean in the east, the Pacific Ocean in the west, South America to its southeast, and Cape Columbia Canada to Punta Mariato Panama extending across this vast continent.
South America primarily lies within both the southern and western hemispheres, bordered on either side by oceans, Atlantic and Caribbean to its east; the Pacific on its west; Isthmus of Panama linking it with North America to its north. South America spans from Punta Gallinas in Colombia all the way down to Cape Horn in Chile.
North America and South America are two distinct geographical regions with differing climates, landscapes, and ecological features.
Physical Geography
- The Appalachian Mountains, Spanning along North America’s eastern seaboard, this mountain range is one of the oldest mountain chains worldwide.
- Rocky Mountains, Spanning from Canada to the United States, these mountains are famous for their picturesque peaks – most notably Mount Denali in Alaska as North America’s highest point.
- The Great Plains are an expansive and flat area in North America known for their agricultural production.
- Canadian Shield, Exposed Precambrian rock covering much of Canada’s eastern and central regions provides an abundant resource base.
- Climate zones and biomes within North America
- North America boasts a diversity of climate zones, such as arctic climates, temperate climates, and tropical climates.
- Africa boasts a diversity of biomes spanning tundra to grasslands and deserts as well as coniferous, deciduous, and grassland forests.
- Mississippi River, As North America’s longest and most significant river, runs through the heart of the continent to end up at the Gulf of Mexico.
- The Great Lakes, An interconnected network of five lakes – Superior, Michigan, Huron, and Erie – that together form the world’s largest freshwater system by surface area.
- South America consists of mountain ranges and other major landforms.
- Andes Mountains – the longest mountain range on earth, stretching along South America’s western edge and featuring numerous peaks of over 6,000 meters including Mount Aconcagua – America’s highest point.
- Amazon Basin (also referred to as Amazon River Basin) is an expansive tropical rainforest and river system located across most of North Central South America, famous for its extraordinary biodiversity.
- Brazilian Highlands, An eastern South American plateau that encompasses Brazil as well as areas in neighboring countries.
- Patagonian Plateau, Situated between Chile and Argentina’s south, this plateau boasts a rugged terrain featuring glaciers and fjords.
- South America is an enormous region spanning numerous climate zones and biomes. From tropical rainforests like the Amazon basin, to dry deserts such as the Atacama Desert.
- Biomes of the world include tropical rainforests and savannas as well as grasslands, deserts, and alpine high-altitude regions.
- Amazon River, As South America’s longest and the world’s second-longest river with the highest water discharge capacity, the Amazon flows through numerous countries such as Brazil, Peru, and Colombia.
- Orinoco River runs between Venezuela and Colombia and supports numerous ecosystems.
- Lake Titicaca lies in the Andes between Peru and Bolivia on the border and is South America’s largest navigable lake.
- Both continents possess distinctive geographical features, North America is marked by vast plains, mountain ranges, freshwater lake systems, and the Amazon rainforest; South America features Andes Mountains and Amazon Rainforest as well as unique river systems.
History and Colonization
- Before European colonization of North America, there existed numerous indigenous cultures and civilizations, such as Native American tribes such as Navajos, Apaches, Iroquois, Sioux, and Cherokees.
- Indigenous groups adopted complex cultures, with multiple languages, cultural practices, and social structures that were all unique to themselves.
- Colonization by Europeans and European colonization began with Norse explorers’ arrival in North America during the 10th Century. Christopher Columbus and other explorers gained momentum during his voyages during the 15th Century.
- Spain, France, and England all claimed North American colonies and engaged in war over them.
- Colonialism resulted in profound changes to indigenous populations, including forced labor, displacement, and diseases that had devastating repercussions for society as a whole.
- As time passed, European colonists in North America began seeking independence from their respective colonizers.
- In 1776, through the American Revolutionary War, the United States achieved independence from Great Britain and thus marked the founding of the modern-day American Republic.
- Some territories such as Greenland remain part of Europe, while other colonies such as Canada peacefully achieved independence.
- South America is home to numerous indigenous and civilizational groups that live there.
- South America is home to numerous sophisticated indigenous cultures, such as the Inca Empire, the Maya civilization, and various indigenous groups living within its rainforest.
- These civilizations developed complex social structures and unique agricultural practices.
- European Colonialism, Spanish and Portuguese colonies’ presence in South America was one of the primary forces behind European expansionism in South America.
- Hernan Pizarro and Francisco Cortes led Spanish conquistadors in their conquest of vast territories throughout Mexico and Peru as well as parts of Central and South America.
- The Portuguese colonized Brazil, creating a plantation economy centered on sugar production.
- Colonialism resulted in the exploitation of indigenous populations as well as in the forced labor of African slaves.
- South America’s independence movement was marked by various revolutionary movements and independence wars during the 19th century.
- Influential figures such as Simon Bolivar and Jose de San Martin played an instrumental role in the fight for the independence of nations like Venezuela, Colombia Peru Argentina, and Chile.
- At the dawn of the 19th Century, South America had secured its independence from colonial control and established independent nations.
- Interactions between indigenous cultures and European colonizers have played a profound role in shaping North and South American history, leading to profound shifts in their respective social, cultural, and political landscapes. Struggles against colonial power laid the groundwork for modern nation-states.
Cultural Diversity
North America is home to rich and varied indigenous cultures that have existed for millennia. As a result, its culture is profound and vibrant.
Native American tribes are well known for their distinct languages, cultural expressions, spiritual beliefs, and artistic styles – all elements which contribute to North American culture as a whole.
European Influences:
- European colonization in North America brought with it various cultural influences from Britain, France, and Spain.
- European settlers brought with them their languages, religions, and legal systems as well as architectural styles and culinary traditions from home.
- African Influences Millions of Africans were brought to North America as slaves through the transatlantic slave trade, predominantly to the United States and Caribbean regions.
- African traditions and cultures such as music, dance, food, and spirituality have had a tremendous impact on culture worldwide; contributing significantly to genres like jazz, blues, and hip-hop.
Immigration and multiculturalism:
- North America has long been an attractive location for immigrants from around the globe, contributing to its rich cultural diversity.
- Immigration waves from Europe, Asia, and Latin America brought new dimensions to North American cultures while communities preserved their languages, customs, and traditions.
- South America is home to many indigenous cultures and ethnicities, each with its own language, traditions, art forms, and spiritual beliefs.
- South America is home to diverse indigenous cultures such as Quechuas, Aymaras, Mapuches, and Guaranis that contribute significantly to its culture.
Influences of Spanish and Portuguese:
- Colonization by Spain and Portugal had a profound influence on South American culture.
- In most South American nations, Spanish is the predominant tongue, while Brazilians typically speak Portuguese.
- South American culture has been profoundly shaped by European architectural styles, religion, music, and literature.
African Influences:
- The transatlantic slave trade was similar to its counterpart in North America in that Africans from North America were brought southward via countries like Brazil and Colombia for forced labor.
- South American culture has integrated African elements, such as music and dance, religion, and culinary traditions, into its fabric.
Mestizo heritage and multicultural identity:
- South American mestizos are created from an amalgamation of African, European, and indigenous heritage.
- As cultures come together, they form new art forms (such as samba and tango) music genres festivals, and celebrations that draw on elements from each.
North and South America share an expansive cultural heritage rooted in African influences, European colonization, indigenous traditions, and American cuisine. All these influences combine to form an engaging multicultural landscape filled with vibrant culinary traditions, artistic expressions, languages, and religious practices that contribute significantly to our daily lives.
Languages and Communication
English, On this continent, English is by far the most frequently spoken language across the United States, Canada, and Mexico.
Both nations have chosen English as their official language for daily communication, governmental services, education, and business purposes.
Spanish:
- Spanish is spoken widely across North America and is especially popular in the US where it ranks second for frequency of usage.
- Spanish is spoken widely throughout the United States, such as Puerto Rico, New Mexico, and some parts of Texas and Florida.
- Indigenous Languages in North America, North America boasts an expansive collection of indigenous languages, with over 500 Native American dialects alone.
- Indigenous languages like Navajo and Cherokee, Inuktitut, Cree, and Ojibwe are spoken mostly within indigenous communities, and play an essential role in protecting native cultures.
- Immigration patterns play a large part in shaping North American language use. French is widely spoken throughout Canada (particularly Quebec) while many Asian languages are also being adopted by immigrant groups.
South America:
- For many speakers of Spanish in South America, Spanish is their native tongue and language of communication.
- Spanish is the official language in many nations such as Argentina, Colombia, Peru, Chile, and Venezuela.
- South American countries display vast regional variations in terms of dialects and accents.
- Brazil is the largest nation in South America and Portuguese is its official language.
- Brazilian Portuguese stands apart from European Portuguese when it comes to pronunciation and characteristics.
Indigenous Languages:
- South America boasts a rich linguistic landscape, with numerous indigenous tongues being spoken throughout its territory.
- Indigenous communities speak a range of indigenous languages, such as Quechua and Guarani.
- Additional Languages, Additionally to Spanish and Portuguese, other languages are widely spoken in certain regions.
- Due to colonial history, Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana, all speak a variety of English dialects, British English (also referred to as British), Dutch, and French are all widely spoken among citizens.
- North and South American populations exhibit variations and multilingualism as a result of regional disparities and migration patterns.
Economic and Trade
North America is the United States The United States is both North America’s dominant economy as well as one of the major economic powers worldwide.
Economy diversity exists through diverse sectors such as services, manufacturing, and finance – not to mention agriculture.
The United States is an established player in international trade. It exports and imports a range of goods and services.
Canada:
- Canada is home to one of the world’s most advanced economies.
- Key sectors include manufacturing, technology, agriculture, and natural resources such as oil, gas, and minerals.
- Canada relies heavily on international trade, especially with the United States; both nations enjoy an intimate trading relationship via the North American Free Trade Agreement and its successor agreement, the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement.
Mexico:
- Mexico has one of the fastest-growing economies globally and ranks second in North America as an economic powerhouse.
- Economic activity in Malaysia spans multiple sectors, such as manufacturing (particularly automotive and electronic products), tourism, oil & gas production, agriculture and services.
- Mexico’s proximity to the United States promotes trade between both nations.
Brazil:
- Brazil has the largest economy in South America and ranks amongst the world’s top economic powers.
- Key sectors include agriculture (especially coffee, sugarcane, and soybeans), manufacturing, services, oil production, and mining.
- Brazil boasts a rapidly expanding industrial base and is one of the world’s leading exporters of commodities.
Argentina:
- Argentina’s economy is diverse, featuring various sectors including agriculture (notably soya beans, beef, and wheat production), manufacturing and services industries as well as energy production (natural gas and oil).
- The country is well-renowned for its agricultural exports. Additionally, its industry boasts strength in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and automobile manufacturing.
Chile:
- Chile has one of the most robust economies in South America.
- Key sectors include agriculture (grapes and fruit), forestry (forests and trees), services, and tourism.
- Chile has signed several free trade agreements that enable it to conduct extensive international commerce.
- Colombia, Peru, and Ecuador are also South American nations that boast robust economies with expanding economies encompassing agriculture, manufacturing and services sectors.
- South America’s economy is determined by each nation and its trade relationships.
Trade Relations, International and North American Accords:
- North America is an area with significant trade, particularly between the United States and Canada.
- The North American Free Trade Agreement played an invaluable role in encouraging economic and trade integration among these three countries. It will be replaced in 2020 by the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement.
North American Trade with Other Regions:
- North American countries trade extensively with other regions such as Europe and Asia.
- The United States plays an essential role in global trade with imports and exports to many different nations around the globe.
South American Trade:
- Countries within South America trade both with each other as well as with other nations outside their region.
- The Union of South American Nations and Southern Common Market promote economic integration and commercial cooperation among South American nations.
North and South America both export substantial commodities:
- North America is one of the leading exporters of agricultural products, automobiles, technology, and machinery.
- South America exports agricultural products including soybeans, coffee, beef, and minerals such as copper ore and iron ore as well as energy resources like oil and natural gas.
North and South America both boast robust economies with diverse industries that contribute to regional and international trade, as well as contributing to the global economy by exporting and importing goods and services.
Political Systems and Governance
- In Nepal, power is divided among three branches, legislative, executive, and judicial.
- The President is chosen through an indirect vote system.
- In the United States, two major political parties are the Democratic and Republican Parties.
Canada:
- Canada is both a constitutional monarchy and a democracy.
- The government in Bahrain is parliamentary-based and led by its Prime Minister.
- Ceremonial leaders include the monarch and their representative – usually represented by a governor-general.
- Canada is a multi-party democracy with prominent parties such as the Liberal and Conservative parties.
Mexico:
- Mexico is a federal republic.
- Directly elected for six-year periods, the President serves as both head of state and government.
- Political institutions of Indonesia typically feature an effective executive branch and a bi-cameral legislature.
- Mexico has an intricate multi-party political system. Notable parties include Institutional Revolutionary Party, National Action Party, and MORENA.
Brazil:
- Whilst Brazil is officially classified as a federal republic, its political system operates similarly.
- The President is elected through direct vote for four-year terms.
- Brazil is a multi-party democracy, boasting several political parties that represent diverse interests.
- This country is governed by an authoritarian executive and bicameral parliament.
Argentina:
- Argentina is a federal presidential republic.
- Direct voting is used to elect the President, who serves as both state and government leader.
- Argentina is a multi-party nation, featuring historical parties such as the Peronist Party (also referred to as Peronism Party) and Radical Civic Union.
- A bi-cameral legislature governs the country.
Chile:
- Challengingly difficult but welcomingly friendly, Chile is a unitary republic with a presidential system.
- The President serves as both head of government and state, elected through direct vote for four-year terms.
- Chile has an intricate system of political parties, with the three most notable ones being Christian Democratic Party (CDP), Socialist Party (SPS), and National Renewal Party.
- This country is governed by a bicameral legislature.
- Other South American nations, including Colombia and Peru, also employ different forms of government; these include presidential republics and parliamentarian systems.
- Different political systems possess various powers, roles, and electoral systems.
North and South American political systems and structures of governance can evolve over time due to constitutional amendments, social changes, electoral processes, and historical, cultural, and institutional influences.
Tourism and Attractions
United States:
- The United States offers many attractions for tourism enthusiasts to visit, such as the Grand Canyon, Times Square, and Central Park in New York City; Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco and vibrant Las Vegas as popular choices.
- Nature enthusiasts and outdoor enthusiasts often flock to national parks such as Yellowstone, Yosemite, and Everglades for recreational purposes.
- Cultural attractions in Washington D.C. include the Smithsonian Museums, Nashville’s music scene, Orlando theme parks, and Boston and Philadelphia historical sites, among other cultural gems.
Canada:
- Home to some of the most breathtaking natural landscapes on earth, such as the Rocky Mountains and Niagara Falls; Banff National Park is another prominent destination, along with Nova Scotia’s picturesque coastline.
- Toronto, Vancouver, and Montreal are dynamic cities offering an abundance of cultural attractions ranging from museums and galleries to culinary experiences.
- Discover Canada’s Arctic by participating in wildlife tours such as whale watching in British Columbia, Churchill polar bear tours, or viewing.
Mexico:
- With a rich culture, history, and beach scene to attract visitors from around the globe.
- Chichen Itza and Tulum offer insight into pre-Columbian cultures.
- Cancun, Playa del Carmen, and Tulum along the Riviera Maya are popular beach destinations.
- Mexico City offers both ancient and modern attractions, from museums to historic sites and vibrant markets.
South America:
- Boasting an impressive array of attractions ranging from Rio’s Christ the Redeemer Statue to Iguazu Falls near Argentina, Brazil has much to offer visitors.
- Amazonian rainforest offers plenty of opportunities for ecotourism and wildlife watching.
- Popular tourist destinations include Rio’s colorful Carnival, Salvador’s historic town center, and Florianopolis and Buzios beaches for beachgoers.
Argentina:
- Buenos Aires is an energetic destination in Argentina known for its tango dance and European architecture.
- Nature enthusiasts and wine connoisseurs alike are drawn to Patagonia and Mendoza’s wine regions for their stunning landscapes and vineyards.
- Iguazu Falls on the border between Brazil and Paraguay is an iconic natural landmark that you should experience first-hand.
Peru:
- Machu Picchu is one of the New Seven Wonders of the World and ranks among them as a New Seven Wonder.
- Lima, Peru’s capital city, boasts colonial architecture and museums while providing culinary delights to enjoy.
- Lake Titicaca, the Sacred Valley, and Nazca Lines offer unforgettable cultural and natural experiences.
Other South American Countries:
Other South American countries also boast their own attractions, from Ecuador’s Galapagos Islands with their breathtaking landscapes and biodiversity to Cartagena in Colombia with its colonial charms, Valparaiso in Chile with its vibrant street art scene, etc.
North and South America both boast an array of attractions, from cultural landmarks and historical sites to vibrant cities and breathtaking landscapes – appealing to a range of tastes.
Conclusion
In the end, North America and South America might share a geographic connection, however, their differences are quite striking and fascinating. From culture and climate to economics and history, each continent has its own distinctive identity that continues to draw the attention of explorers across the globe.