Tobramycin and Terramycin are two distinct antibiotics with their own set of unique properties and uses. Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic commonly employed against bacteria affecting respiratory systems, skin conditions, or the urinary tract.
Terramycin’s mechanism involves inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis, due to its broad spectrum action, it may also be prescribed for eye diseases and skin conditions specific to them. Antibiotics are drugs designed to interfere with bacterial protein synthesis.
While both medications serve the same purpose of fighting bacteria, their individual mechanisms, spectrums of effectiveness, and suggested uses differ significantly – understanding this distinction is critical for effective decision-making as well as patient treatment.
Tobramycin
- What is tobramycin?
Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections of the lower respiratory tract, urinary tract, skin structures, and cystic fibrosis of bacterial origin. It is mainly derived from Streptomyces spp. obtained and has a broad antibacterial spectrum of action against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
More importantly, naturally antibiotic-resistant bacterial species that cause chronic cystic fibrosis, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, are targeted with inhaled Tobramycin
Tobramycin was approved by the FDA in 1975. In addition to the inhaled form, ophthalmic and intravenous forms are also available for the treatment of various bacterial infections.
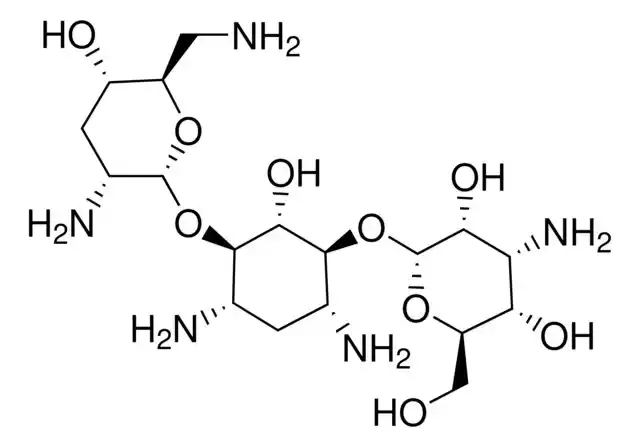
Tobramycin is an antibiotic containing a 4,6-disubstituted 2-deoxytreptamine ring that binds tightly to the bacterial membrane. Upon binding, membrane permeability increases and additional tobramycin diffuses into the cytoplasm and targets 30S ribosomes.
As a result, mistranslated proteins are produced and integrated into the plasma membrane, allowing more tobramycin to enter cells and become bactericidal. Tobramycin is inhaled in CF patients and distributed to 85 central compartments. The drug does not bind to serum proteins and is not metabolized. The unchanged drug is mainly excreted in the urine.
- Use of Tobramycin
Tobramycin ophthalmic is used in the eye to treat bacterial eye infections. Tobramycin works by killing bacteria. Tobramycin ophthalmic can be used alone or together with other medicines for eye infections.
Terramicina
- What is Terramycin?
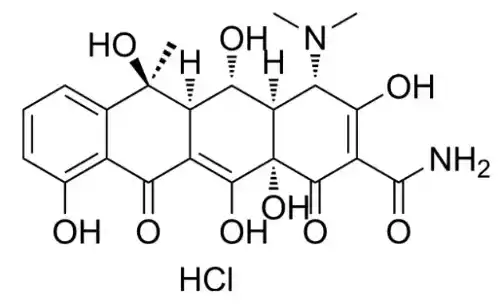
Terramicina is the trade name of an antibiotic eye ointment with the active ingredient oxytetracycline, which belongs to the tetracycline group.
This antibiotic is prescribed for a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Due to its lipophilic nature, terramycin readily crosses the plasma membrane and reversibly binds to 30S ribosomes.
This interaction inhibits protein translation by preventing aminoacyl-tRNA from binding to the 30S ribosome, thereby inhibiting bacterial cell growth.
Terramycin is mainly used in eye preparations in the form of ointments and eye drops to treat eye infections. In addition to ophthalmic use, Terramycin can be found in a variety of oral or topical formulations to treat respiratory, urinary tract, skin, and soft tissue infections.
- Use of Terramycin
Terramycin is used to treat superficial eye infections. Terramycin contains two different antibiotics, oxytetracycline, and polymyxin. Oxytetracycline belongs to a group of medicines called tetracycline antibiotics.
Tobramycin and terramycin: Are they Same?
- Tobramycin and Terramycin are distinct antibiotics with distinct characteristics and applications, each offering something unique for certain conditions. Tobramycin falls under the aminoglycoside category of antibiotics and can treat infections that affect respiratory health as well as urinary tract health, Terramycin on the other hand falls into the oxytetracycline category and treats infections related to eye disorders or skin conditions.
- While both medications target bacteria, their mechanisms of action, target bacteria species, and medical contexts separate them, medical professionals take note of such differences for maximum efficiency in making treatment decisions with optimal outcomes and results for their patients.
Difference between tobramycin and terramycin
The critical difference between tobramycin and terramycin is that tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that interferes with bacterial protein translation by binding to the 16S rRNA in helix 44 (h44) near the A site of the 30S ribosomal subunit. Meanwhile, terramycin is the trade name of oxytetracycline, which interferes with protein translation by preventing the aminoacyl-tRNA from binding to the 30S ribosome.
Tobramycin and Terramycin are broad-spectrum antibiotics used to treat infections caused by gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria with similar mechanisms of action. Both antibiotics interfere with bacterial protein synthesis by targeting different 30S ribosome binding sites. Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside and terramycin is the trade name of oxytetracycline, which belongs to the tetracycline class of antibiotics.
Tobramycin is often used to treat serious infections caused by germs such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Conversely, terramycin is primarily used in ophthalmic preparations to treat eye infections such as conjunctivitis and corneal ulcers.
Table:
| Aspect | Tobramycin | Terramycin |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic Class | Aminoglycoside | Oxytetracycline |
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis | Inhibits bacterial protein synthesis |
| Spectrum of Activity | Primarily effective against Gram-negative bacteria | Broad-spectrum effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria |
| Common Uses | Respiratory and urinary tract infections | Eye infections, skin issues, respiratory infections |
| Route of Administration | Intravenous, inhaled, ophthalmic | Oral, ophthalmic, topical, injectable |
| Bacterial Resistance | Developing resistance in some bacterial strains | Resistance has developed in some bacteria |
| Potential Side Effects | Nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity | GI upset, photosensitivity, the potential for bacterial resistance |
| Special Considerations | Dosing requires monitoring due to toxicity risk | Avoid in children under 8 and pregnant women |
| Availability | Available in various formulations | Available in different formulations |
Which antibiotic is best From tobramycin VS terramycin?
That depends entirely on its application in specific circumstances. Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic with proven effectiveness against Gram-negative bacteria, while Terramycin and Tobramycin offer protection from Gram-positive pathogens as well.
Effective and rapid in its actions, Amoxicillin can quickly address even severe infections, Its use should be limited due to the potential for nephrotoxicity and Ototoxicity.
Terramycin is an oxytetracycline medication with broad-spectrum activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, typically used to treat eye infections, skin conditions, and respiratory tract issues. Unfortunately, bacteria resistance could reduce its effectiveness over time.
Selecting two antibiotics should depend upon the nature of an infection, patient sensitivity, and possible adverse side effects. A healthcare expert should then make their selection based on individual conditions such as bacteria sensitivity and the overall health status of an individual patient.
What are the Best alternatives to tobramycin and terramycin antibiotics?
Alternatives to Tobramycin and Terramycin depend on factors like infection type, susceptibility to bacteria, as well as individual health considerations.
Here are some potential alternatives for each:
Alternative to Tobramycin:
- Gentamicin: Gentamicin like Tobramycin, is an aminoglycoside antibiotic commonly used to treat similar conditions.
- Ciprofloxacin: Ciprofloxacin is an oral fluoroquinolone antibiotic effective against various bacteria types and often prescribed to treat urinary tract infections or respiratory tract infections.
- Amikacin: Amikacin is an aminoglycoside with a broad spectrum that makes a practical choice when resistance Tobramycin resistance becomes an issue. Additionally, this antibiotic serves as an alternative to Terramycin.
Alternative to Terramycin:
- Doxycycline: Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum Tetracycline antibiotic with multiple activities, similar to Terramycin in use and effectiveness.
- Erythromycin: Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic with wide-ranging effectiveness against various kinds of bacteria such as those responsible for respiratory and skin infections.
- Clindamycin: Clindamycin is an antibiotic prescribed to treat various bacterial infections of soft tissues and skin.
Final Thought About – Tobramycin vs. Terramycin
Tobramycin and Terramycin are two antibiotics that treat a wide range of bacteria. Tobramycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that interferes with the translation of bacterial proteins by binding to the 16S rRNA in helix 44 (h44) near the A site of the 30S ribosomal subunit.
Terramycin, the trade name for oxytetracycline, prevents aminoacyl-tRNA from binding to the 30S ribosome, thereby inhibiting protein translation.
Tobramycin is active against some bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. At the same time, Terramycin has a broader spectrum of action and is effective against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Tobramycin is commonly used for severe systemic infections, including respiratory tract infections, while terramycin is mainly used for eye infections such as bacterial conjunctivitis and corneal ulcers. Therefore, when choosing the right antibiotic for bacterial infections, the difference between tobramycin and terramycin should be considered.